7.4.7 If you diagnose asphyxia, start resuscitation!
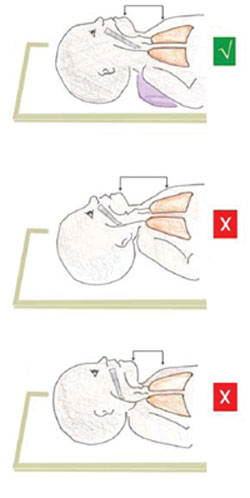
Position the newborn on his or her back with the neck slightly extended as shown in the top picture in Figure 7.11. Open the airway by clearing the mouth and nose with suction using the bulb syringe as you saw previously in Figure 7.9.
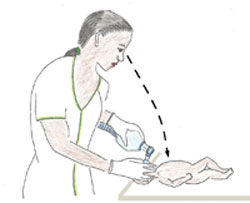
- Position yourself at the head of the baby (see Figure 7.12).
If the apical heartbeat is > (more than) 60 beats/minute:
- Ventilate with the appropriate size of mask and a self-inflating ambu-bag. The mask should be fitted as shown in Figure 7.13. Make a firm seal between the mask and the baby’s face, so air cannot escape from under the edges of the mask. But don’t force the mask down onto the baby’s face, because this could push its chin down towards its chest (bottom diagram in Figure 7.11) and compress its airway.
If the apical heart beat is < (less than) 60 beats/minute:
- Apply heart massage (look back at Figure 7.4) and ventilate alternately (on and off ventilation) with the ambu-bag.
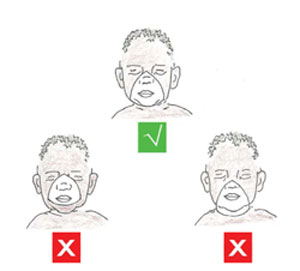
7.4.6 Apply gentle tactile stimulation to initiate or enhance breathing
