9.5.1 Fistula
Fistula is an abnormal opening (usually as a result of ruptured tissues) between the:
- Vagina and the urinary bladder
- Vagina and rectum
- Vagina and urethra (the tube bringing urine from the bladder to the opening in the vulva)
- Vagina and ureter (the tube bringing urine from each kidney to the bladder).

As a result of the fistula, urine or faeces get into the vagina and exit in an uncontrolled way. A woman with a fistual can leak urine or faeces while walking, or doing any daily activities, and the waste stains her clothes and creates a bad smell (Figure 9.5). Because of these effects, her husband and family may stigmatise her or make her an outcast. You can also imagine what continuously leaking urine or faeces means at a personal level. Other consequences of fistula may include constant depression, and many physical illnesses and infections of the reproductive tract, bladder and kidneys, which may even result in the woman taking her own life.
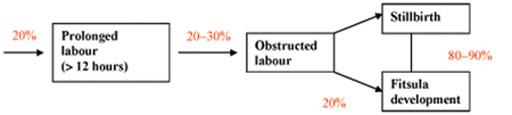
Obstructed labour is responsible for about 20% of all cases of fistula formation (see the research study reported in Figure 9.6).
Other rare causes of fistula are congenital malformation (abnormal communication, usually between the rectum and vagina, found at birth), infection (specifically tuberculosis), trauma, forceful sexual intercourse (rape), and early age sexual intercourse.
9.5 Complications resulting from obstructed labour
