2.4 The importance of attachment theory
Attachment continues to be an important psychological idea that helps to describe the quality of the relationship between the child and key caregivers in a variety of different care settings.
The most effective way to visualise attachment is as a process. Through the development of close, caring and positive relationships in childhood, a young child can build up an effective internal set of ideas or what has been called an ‘internal working model’ (Bowlby, 1969) of how they see themselves, how they interact with others, and also how they develop their own sense of who they are and who they can become within the social world around them.
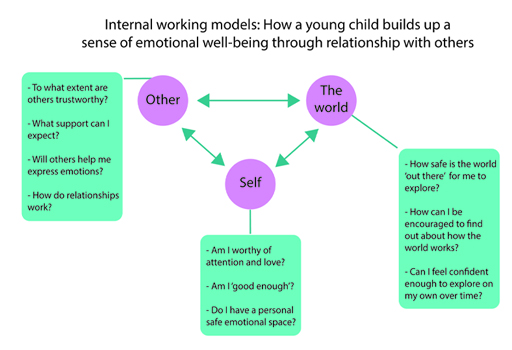
Figure 5 is a diagram showing the interconnections between self, other and the world in order for the young child to build up an internal working model of how relationships work.
Reflecting on the diagram and the questions that might be asked or addressed through different interactions, you might notice how different ways of being attached or connected to significant others, especially as a young child, will have an enormous effect on that child’s perceptions. The components and quality of the different interactions will not only affect how the child perceives themselves and their own value in the world, but also whether they believe they are ‘worthy’ of affection and care from others.
Therefore, a young child who has experienced consistent and warm, loving connections with significant caregivers who have been attuned to their emotional needs will have been given ‘positive acceptance’ for who they are. They are then more likely to grow up feeling they are ‘worthy’ in terms of long-term relationships, in particular intimate relationships, and will be able to express their emotions more openly. They are also better prepared to make positive contributions to relationships with others in the future. The emotional security they experienced as a child is likely to lead to a greater understanding of a range of emotional reactions to different situations. Infants that are securely attached are not only more likely to have greater empathy for others, but also higher tolerance of being left alone for longer periods of time, away from significant others.