2 Other ways to kill bacteria
Unlike quorum sensing, some antibiotic alternatives are bactericidal. Just like the bactericidal antibiotics you looked at in Week 2, these treatments work by killing the bacteria that cause infections.
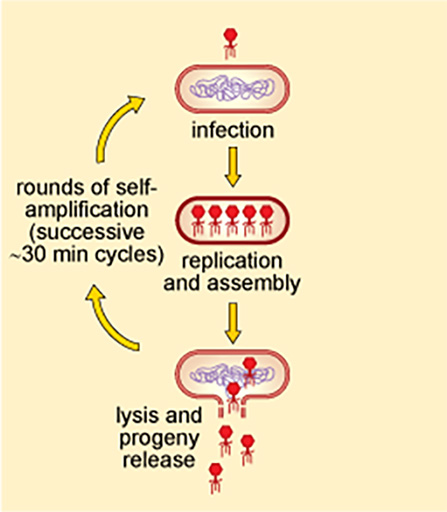
In Week 4, you learned about the horizontal gene transfer mechanism of transduction. In this process, DNA is transferred between bacteria via infection with viruses known as bacteriophages.
Bacteriophages can also be exploited to treat infections. When bacteriophages infect bacteria, they replicate and assemble new virus particles, before lysing (bursting) and killing the bacteria, releasing the new bacteriophage particles (Figure 4).