Freshwater rewilding
1 Rivers
1.9 Rewilding riverbanks
Rewilding the banks of the rivers is also an important aspect of rewilding rivers as it helps to re-establish the natural processes and biodiversity that are essential for healthy aquatic ecosystems.
Riparian zones are the areas adjacent to rivers and streams and they are important areas in rewilding. Riparian vegetation supports a diverse array of wildlife, offering food and shelter to birds, insects and mammals. The roots of riparian plants help to stabilise soil and reduce the impact of floods, while their foliage provides shade that keeps water temperatures suitable for aquatic life.
Measures to rewild riverbanks include allowing natural regeneration to occur and leaving fallen deadwood lying in rivers. Flood waters can deposit seeds, dead leaves and wood from upstream, enriching the soils with nutrients and bringing new species to the area. As with the forests and grasslands you learned about in Module 5, grazing, trampling and browsing are important here too as they also disperse seeds and create and maintain a diverse mosaic habitat.
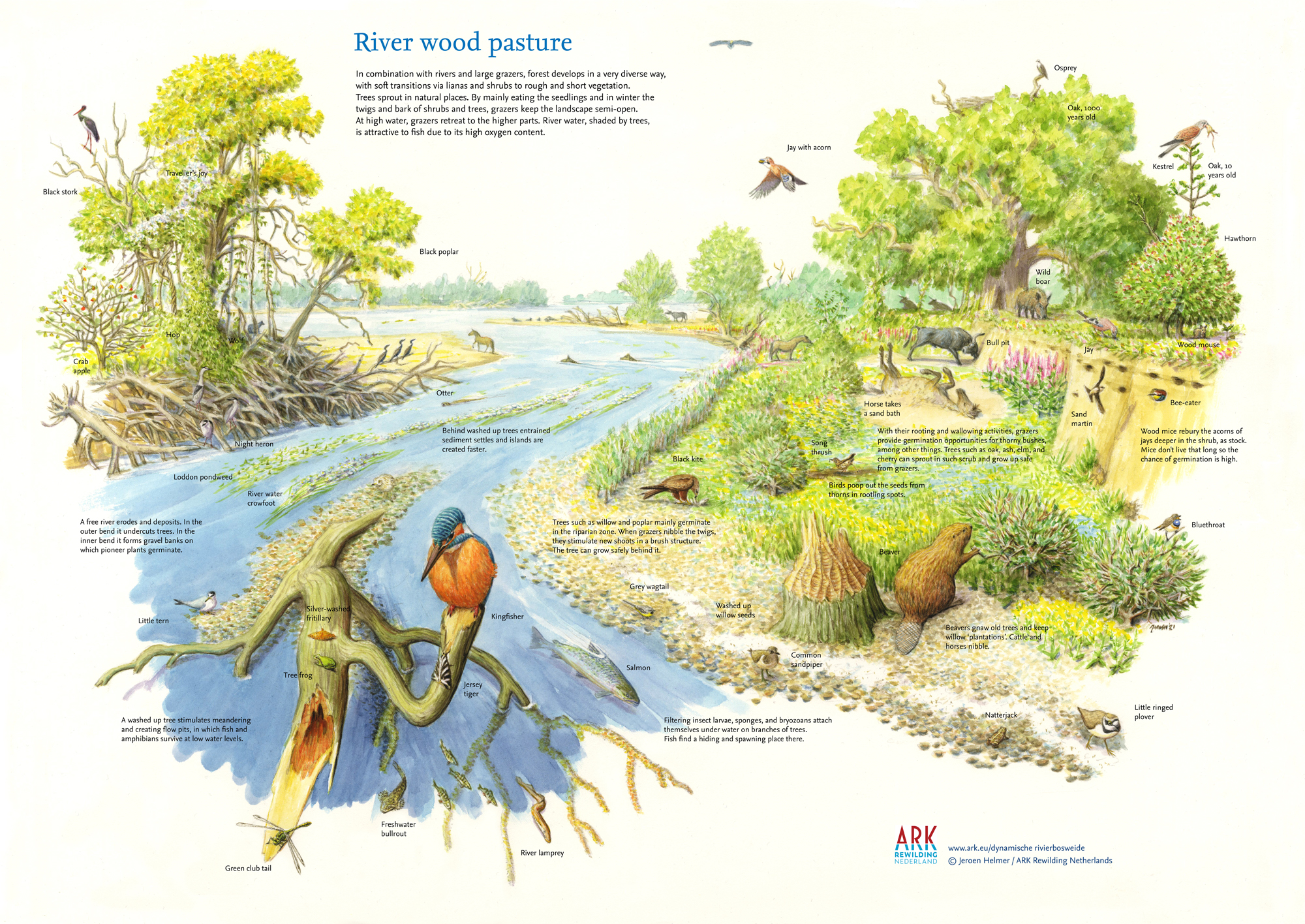
River wood pasture. Credit: Jeroen Helmer / ARK Rewilding Netherlands.
Click here for an enlarged version of the above image.
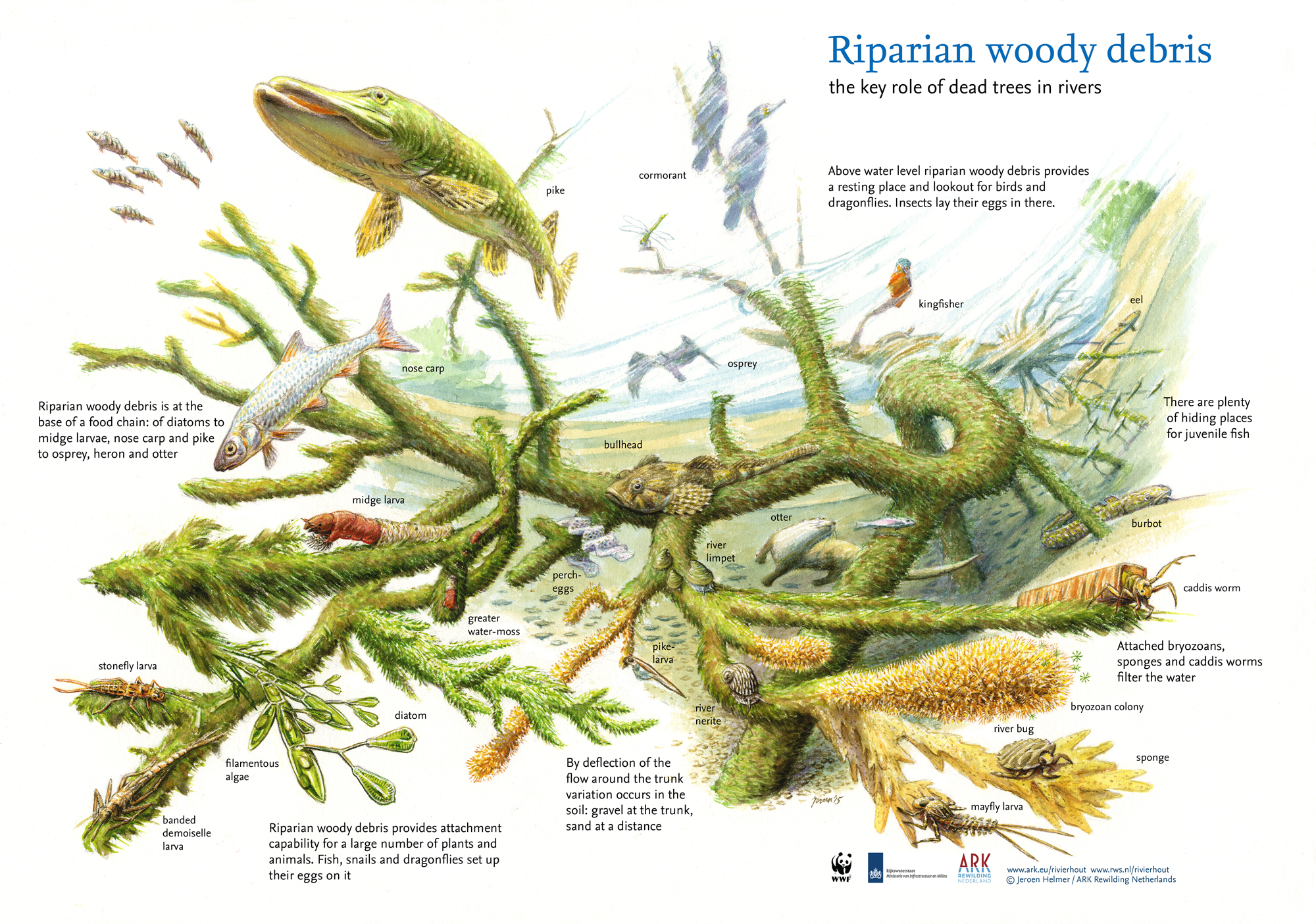
River (riparian) wood debris and their role. Credit: Jeroen Helmer / ARK Rewilding Netherlands.
Click here for an enlarged version of the above image.

The water buffalo: A Keystone species. Credit: Jeroen Helmer / ARK Rewilding Netherlands.
