Glossary
- BMD
- bone mineral density, measured by DXA scan. It is usually expressed as a T-score, which indicates how far the patient’s BMD is below (or above) the young woman average.
- DXA
- dual energy absorptiometry scan which measures BMD. It is very low radiation (comparable to background levels) and takes a few minutes. Patients must be able to get on and off a couch.
- Osteoporosis
- meaning ‘porous bones’. It is used to refer to the condition of reduced bone strength in adulthood which makes bones more fragile and easily broken. It is also used to refer to a condition of low measured bone mineral density (BMD), below the normal range of a young woman’s BMD on a DXA scan.
- Osteopenia
- where DXA results are between 1 and 2.5 SD below the young adult mean.
- Secondary osteoporosis
- where specific medical conditions play a significant role in reducing bone mineral density. This is different to primary osteoporosis, which relates mainly to age, genetic predisposition, and diet and lifestyle factors.
- Osteoblast
- these bone cells create new bone by secreting a collagen and mineral matrix.
- Osteoclast
- these bone cells resorb old or damaged bone, by dissolving it.
- Osteocyte
- these bone cells sense bone loading and orchestrate the activities of the other cells.
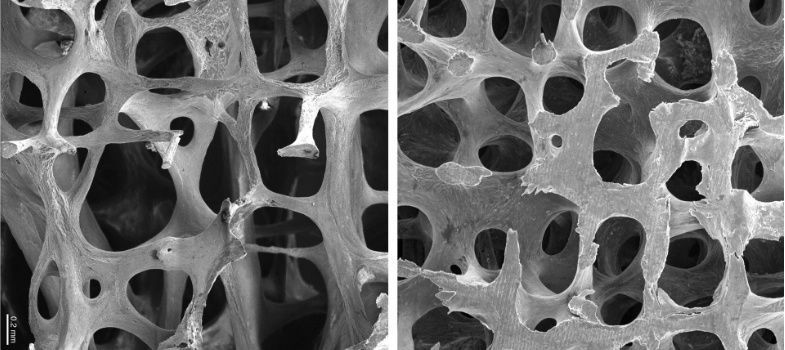
- Trabecular bone
- this consists of a honeycomb-like network of interconnecting bone tissue, interspersed with spaces filled with bone marrow.
- Cortical bone
- this bone is denser, made of smooth layers of bone tissue and nourished by blood vessels. It forms the outer structure of bones.
- Androgen
- a term for male sex hormone, predominantly testosterone.
- FRAX
- a fracture risk assessment tool recommended by NICE. It links to National Osteoporosis Guidelines Group (NOGG) guidance.
- Qfracture
- a fracture risk assessment tool recommended by NICE. It is not linked to any specific treatment advice.
- NOGG
- National Osteoporosis Guidelines Group – a multidisciplinary group created to provide guidance to users of the FRAX tool. Its processes are accredited by NICE.
- Major Osteoporotic Fracture (MOF)
- this term encompasses hip, spine, wrist or humeral fractures
- Anti-resorptive
- a drug which reduces the action of osteoclasts in the bone, tipping the balance of activity towards formation
- Bisphosphonates
- the commonest osteoporosis treatments, acting on osteoclasts as anti-resorptives. They are available as oral or intravenous preparations.
- Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ)
- a rare side effect of bisphosphonate therapy, seen mainly in high dose anti-cancer use, in which the gum fails to heal over exposed bone.
Back to previous pagePrevious
5 Summary