4.1.1 Standard procedures for giving safe injections
First, you should always follow the standard procedures (also known as universal precautions) for preventing infection and injury when you are giving an injection.
What standard procedures should you take before giving an injection?
Standard procedures are described in several parts of this curriculum, including the Antenatal Care, Labour and Delivery Care, and Communicable Diseases Modules.
You should:
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water, and allow them to ‘air dry’.
 Figure 4.1 A standard safety box. (Photo: Basiro Davey)
Figure 4.1 A standard safety box. (Photo: Basiro Davey) - Prepare all the equipment you need and lay it out on a clean tray that has been swabbed with antiseptic solution.
- Organise your equipment to minimise the risk of injury from needles and broken glass.
- Make sure there is a safety box nearby for the safe disposal of used syringes and needles (Figure 4.1).
- Make sure that children are securely held by someone they know and trust, in the correct position to enable you to give the injection (Figure 4.2). You cannot hold the child because you need both hands to give the injection.
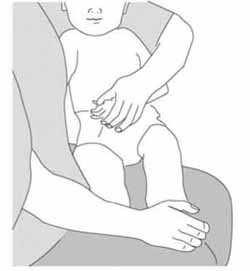 Figure 4.2 The mother or another caregiver should hold the child securely like this. (Source: WHO, 2004, Immunization in Practice, Manual 4, Ensuring Safe Injections, Figure 4-D)
Figure 4.2 The mother or another caregiver should hold the child securely like this. (Source: WHO, 2004, Immunization in Practice, Manual 4, Ensuring Safe Injections, Figure 4-D) - The skin at the site of the injection should be swabbed cleaned with an appropriate antiseptic solution. After giving the injection, press a clean cotton swab onto the site until all bleeding stops.
You will learn about these and other immunization safety issues in more detail in Study Session 7.
4.1 Preparing to give injectable vaccines
