3.1 Using cryptography to prove identity
This section is part of the amber and green pathways.
Cryptography isn’t just used to hide secrets, it can also be used to authenticate data sent on an insecure network – such as the internet. The process begins by checking that your copy of a piece of data is an exact match for the one you requested.
Hashing
Hashing is the mathematical process of converting data of any size into data of fixed length known as the ‘hash’ (alternative names include message digest, hash codes, hash sums or hash values).
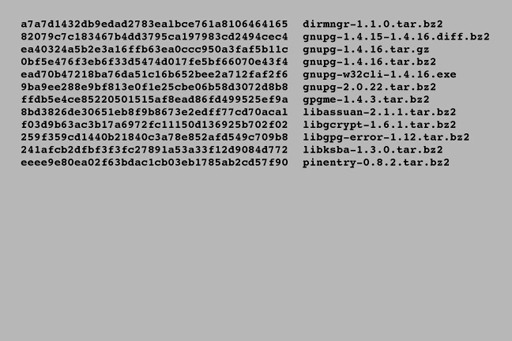
Hashing operates in one direction only, making it impossible to deduce the original data from the resultant hash. The intention of hashing is not to preserve the contents of the data but to create a unique identifier for every single piece of data. When a file is published on the internet, the author may choose to publish the hash value for that file. For instance, here is some information published by the GnuPG encryption software authors on their website:
Each long line of numbers and letters on the left is a hash (in this case from a hashing program called SHA-1), the text on the right is the name of the file. If you download one of these programs, you can then run your own copy of SHA-1 on your download and obtain a hash – if your file exactly matches the original the two hashes will be identical. Even a minimal tampering of either the file contents or the hash is flagged with a mismatch of the hash when calculated.
A variation of a single bit of data between two otherwise identical files will result in vastly different hash values, so any edits to a file between two hashing operations will result in different hash values revealing that the data has been tampered with and should not be trusted.
A large number of hashing algorithms have been developed; the most widespread are algorithms called MD5, SHA-1 and SHA-2. Although MD5 and SHA-1 are in common use, both have been found to be flawed. Under certain circumstances ‘collisions’ can occur where two pieces of different data can generate the same hash value (albeit under specifically controlled conditions).
This weakness in the MD5 hashing algorithm has been used in malware targeting Microsoft Windows computers. Since neither algorithm can be guaranteed to generate unique hashes they can be considered ‘broken’ and should not be used. The United States government requires all hashes to be generated using the newer SHA-2 algorithm which has not shown any such weaknesses.
Activity 2 Get started with crytography
Visit the website http://icyberchef.com [Tip: hold Ctrl and click a link to open it in a new tab. (Hide tip)] . Cyberchef is a simple, intuitive web app for encoding and decoding data without having to deal with complex tools or programming languages. You can play with some common encoding algorithms. Try the following exercise to get started with Cyberchef and to understand the basics of cryptography – you can then play with a variety of encryption techniques and compare them.
- a.Encode the string ‘Cyber Security’ to Base64. What is the output?
- b.Encode the string ‘Open learn’ to Hex. What is the output (with spaces)?
- c.To the hex output for ‘Open learn’, add a hashing function in the recipe (MD5, SHA-1 or any other). What is the output now?
Answer
- a.Q3liZXIgU2VjdXJpdHkK
- b.4f 70 65 6e 20 6c 65 61 72 6e
- c.For SHA-1, hash, 3d04faee258aa313a2badfb56620a4f7b0de48b0
Next, you’ll find out how digital signatures and certificates use cryptography.