1 Measuring antibodies by ELISA
ELISA is a very versatile assay used for measuring antibodies against pathogens in serum and body fluids. Variants of the assay are used to measure autoantibodies and cytokines. In this course, you will use a standard ELISA to measure antibodies against SARS-CoV2 in serum samples.
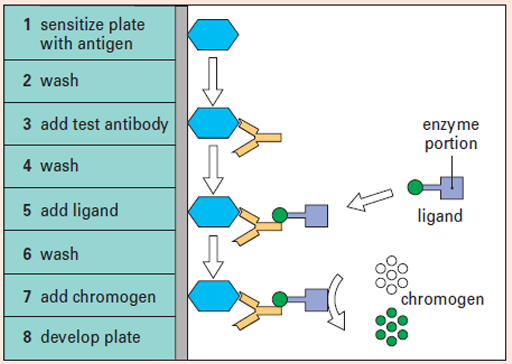
ELISAs are usually carried out on 96-well plastic plates which have been ‘sensitised’ by binding an antigen to the surface of the wells. You can see the basic steps in an assay outlined in Figure 1.
The antigen bound to the plate determines the specificity of the ELISA test; e.g. SARS-CoV2 spike protein on the plate detects antibodies that are directed to spike protein. The test sera are applied to the plate in serial dilutions as explained in a video guide that you will watch later. A variety of ligands can be used to detect the bound antibodies. The two most often used are a second antibody which binds the first antibody or an antibody-binding protein (protein-G). A variety of enzymes may be coupled to the ligand; the two most often used are horse-radish peroxidase (HPO) or alkaline phosphatase. The chromogen must be matched appropriately to the enzyme.
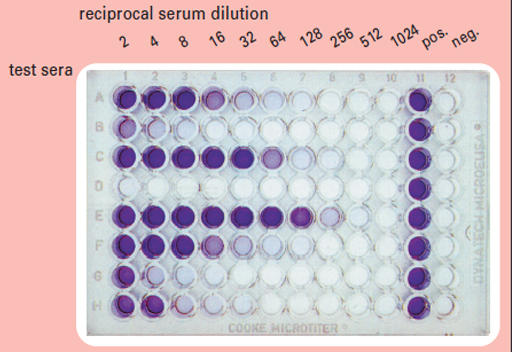
In these experiments, any antibodies that have bound will be detected with a second antibody coupled to horse-radish peroxidase (HPO), and the chromogen is a substance called tetra-methylbenzidine (TMB), which generates a blue end-product. The enzyme also requires hydrogen peroxide as a substrate. An example of a developed plate is shown in Figure 2. Do not be concerned if you do not understand the results shown in this figure − how to interpret the results will be explained later.