2.1 Serology
Serology is the study of antibodies in blood serum and body fluids. It also relates to how antibodies can be used to distinguish between different pathogens and different strains of a pathogen. Serum, in this context, is the fluid component of blood containing soluble molecules such as antibodies and other proteins. Serum is formed after blood has clotted, removing the cellular elements of blood (red cells, white cells) and other components involved in formation of the clot (platelets and proteins of the blood clotting system).
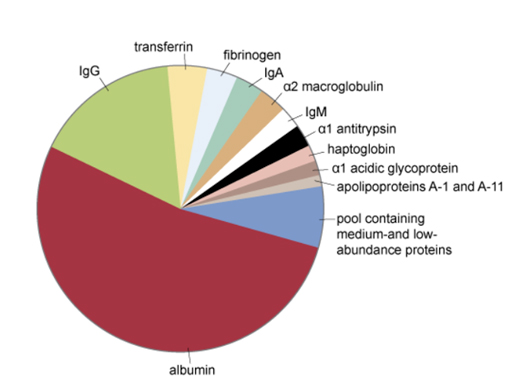
Serum should be distinguished from blood plasma which lacks cells, but which retains the components required for clotting. The pie chart in Figure 2 shows the relative amounts of the proteins in plasma.
As you can see, the three major classes of antibody (IgG, IgA, IgM) constitute about 25% of the total plasma protein.