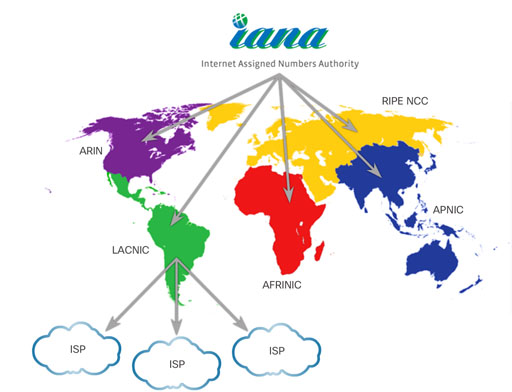
2.2.7 IP address management
On the internet, each IP address must be unique. The Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA) is responsible for controlling the distribution of IP addresses so that there is no duplication. IANA allocates blocks of IP addresses to one of five regional internet registries (RIRs). ISPs obtain blocks of IP addresses from the RIR in their geographic region. It is the responsibility of the ISPs to manage these addresses and assign them to customer networks and end users’ devices and networks.
The ISP determines where to forward the traffic. Packets are passed from router to router, possibly through multiple ISP networks, until they reach their final destination. Routers in each of the ISPs use the destination address of the IP packets to choose the best path through the internet. The packet switching is transparent to the user, as they only see what was sent and received.
