1.1 From genetic information to protein function
Almost every process in a cell requires proteins. As you saw in Week 2, antibiotics often exert their bactericidal and bacteriostatic effects by binding to proteins that are crucial to the structure or function of the bacterial cell.
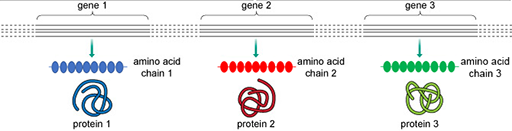
The function of a protein is largely determined by its structure. Proteins are comprised of building blocks called amino acids. The sequence of these amino acids determines the structure of a protein. The
In 1958, Francis Crick, who helped discover the structure of DNA, proposed the central dogma to explain how genetic information, encoded in DNA, can be converted into a functional product, a protein. The following short video gives an overview of this central dogma. Note that the conversion of information, encoded in DNA, into a protein occurs via an intermediate molecule called