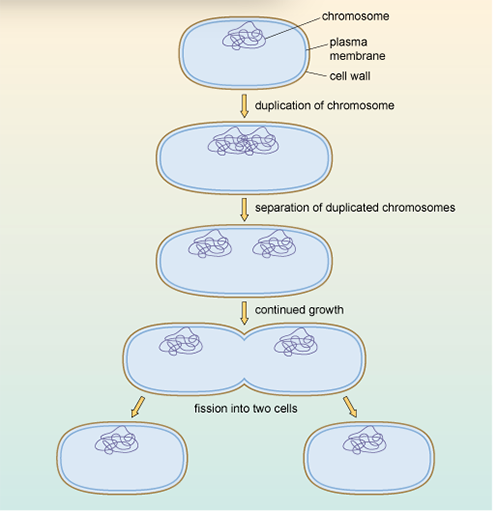
1.3 Transmission of mutations by vertical gene transfer
Activity 1 Exploring vertical transmission
Begin by watching the following animation which illustrates the process of binary fission in E. coli. Then complete the activity below.
Transcript: Video 3 Binary fission in E. coli.
Apply what you have learned and the information about binary fission in the animation to complete the following sentences. Select the appropriate word from the list.
a.
identical
b.
similar
c.
different
The correct answer is a.
Answer
During binary fission, the genetic material (DNA) is copied so that each new daughter cell inherits an exact copy of the parent cell's DNA.
a.
sometimes
b.
never
c.
always
The correct answer is c.
Answer
During binary fission, the genetic material (DNA) is copied, so that each new daughter cell inherits an exact copy of the parent cell’s DNA. When the parent DNA is copied during binary fission, any genetic mutations will also be copied, and consequently inherited, by both of the daughter cells.
a.
sometimes
b.
always
c.
never
The correct answer is b.
Answer
During binary fission, the genetic material (DNA) is copied, so that each new daughter cell inherits an exact copy of the parent cell's DNA. When the parent DNA is copied during binary fission, any genetic mutations will also be copied, and consequently inherited, by both of the daughter cells. If these genetic mutations give rise to antibiotic resistance in the parent bacteria, they will also result in antibiotic resistance in both of the daughters.
Vertical gene transfer is only one of the ways in which bacteria can spread antibiotic resistance genes. In the next section you will look at another – horizontal transfer.