2.2 Conjugation
In the process of conjugation, plasmids are transferred between two contacting bacteria via a hollow tube or pilus (Figure 7).
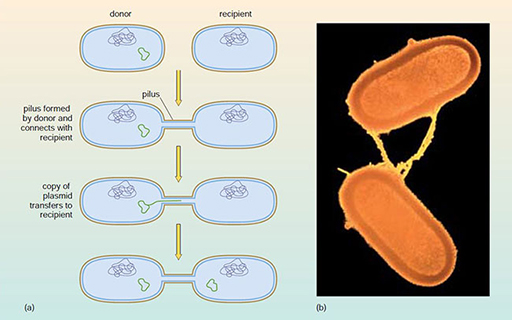
Since antibiotic resistance genes are often located on plasmids, conjugation can result in the transfer of antibiotic resistance from one bacterium to another.
