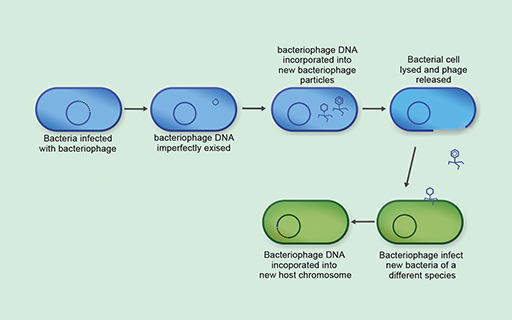
2.4 Transduction
The final mechanism of horizontal gene transfer you will look at is
Viruses that infect bacteria are called bacteriophages
Activity 2 Comparing horizontal transfer mechanisms
Below are some incomplete sentences. Type in the missing words using the following list of words:
horizontal, binary fission, vertical, conjugation, transformation, transduction, plasmid, chromosome, vertical gene transfer.
Answer
Horizontal gene transfer can occur between bacteria of the same generation but vertical gene transfer requires binary fission.
Answer
Conjugation is the only mechanism of horizontal gene transfer that requires direct contact between the donor and recipient bacteria.
Answer
Conjugation, transduction and transformation can occur between bacteria of different types.
Answer
Transduction is the only mechanism of horizontal gene transfer which requires a virus known as a bacteriophage.
Answer
The bacterial genetic element transmitted by horizontal gene transfer is called a plasmid.
You will return to look at some specific examples of how genetic mutation and horizontal gene transfer can result in acquired resistance in the case study of cephalosporin antibiotics at the end of this week. Next you will look at how antibiotic resistance has developed through evolution and natural selection.
