1.1 Natural antibiotics
Most natural antibiotics were discovered before the 1970s, using systematic
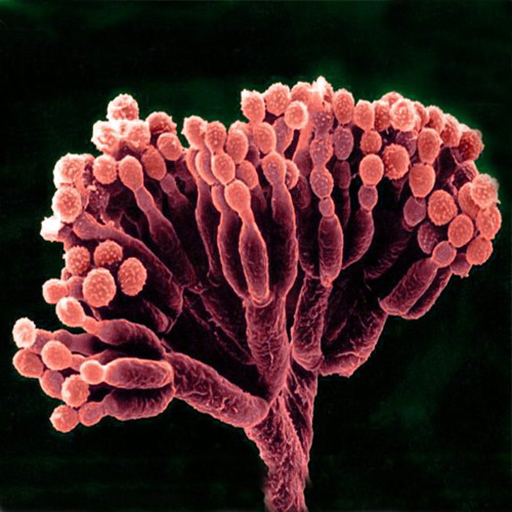
Two types of fungi – the Penicilliums and the Cephalosporiums – have proved good sources of antibiotics. For example, Penicillium notatum (Figure 1) was the source of the original penicillin discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1928. Cephalosporium acremonium gave rise to the first-generation cephalosporins (Clegg, 2015) .
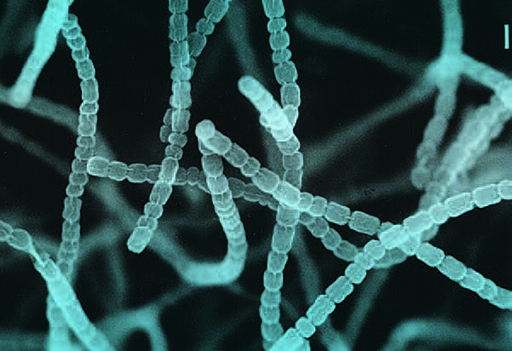
Natural antibiotics isolated from Streptomyces bacteria (Figure 2) include streptomycin, tetracycline, vancomycin, erythromycin and chloramphenicol (de Lima Procopio et al., 2012).