3.2.1 Reverse osmosis
You are probably familiar with this process already, although you may not have heard this particular term. Reverse osmosis is, not surprisingly, the reverse of the normal process of osmosis, which occurs within the human body to allow water to move into and out of your cells and keep you alive.
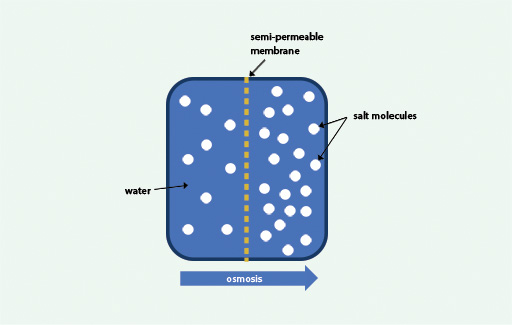
During osmosis, molecules of a solvent (such as water) pass through a semi-permeable membrane from a less concentrated solution into a more concentrated one so as to equalise the concentrations on both sides of the membrane.
A semi-permeable membrane is one which allows the passage through it of water and some other very small molecules but prevents the passage of larger molecules. If you consider a concentrated salt solution to have a high concentration of salt and a lower concentration of water, then you can also think of osmosis as being the movement of water from the area of its high concentration to an area of its lower concentration across a semi-permeable membrane. This is illustrated in Figure 2.
After certain dental procedures, the risk of bacterial infection is high. Based on your knowledge of the process of osmosis, why do you think dentists encourage you to rinse your mouth with a salt water solution?
The salt water solution contains a high concentration of salt and a low concentration of water relative to any bacteria which might be growing around the affected area. So water will be drawn out of the bacteria into the salt water solution (so from a high concentration of water in the bacteria to a lower concentration in the salt solution) to equalise the concentration. The removal of the water from the bacteria causes them to dehydrate and prevents them from multiplying, so the chances of infection is reduced.
The process of reverse osmosis is used in water purification technology, where a semi-permeable membrane filter is used to remove ions, molecules and larger particles from drinking water. Kits containing semi-permeable membranes are commercially available to install in your home to remove a wide range of contaminants from your drinking water including pesticides, bacteria, microplastics, microfibres, heavy metals, fluoride and other pollutants. Reverse osmosis is also used to desalinate sea water (by removing salt molecules from the water) and is widely used in places such as the Canary Islands to provide the rain-deficient islands with potable (drinkable) water from the surrounding Atlantic Ocean.
Activity 2 Reverse osmosis
Based on your understanding of the process of osmosis, write a statement to represent the movement of water in reverse osmosis.
Discussion
In osmosis, water moves from a high concentration of water to a low concentration of water. In reverse osmosis, water moves from a low concentration of water to a high concentration of water.
In order to work against the natural process of osmosis, pressure must be applied to force the water to flow against its natural path. One option, therefore, for the removal of alcohol from beer is to apply pressure of between 20 and 40 bar to the beer, pushing it across a semi-permeable membrane. Due to the pressure the small molecules, such as water and alcohol, are pushed through the membrane whereas the larger molecules, such as flavours, colour and protein, are unable to pass. Thus the alcohol is removed from the beer. Fresh water is then added to the beer after this filtration to restore the volume, and the flavour of the beer can be enhanced by adjusting carbon dioxide levels or by using hop extract or other flavour enhancers.
