2.3 Area of a circle
You have already practised using the formula to find the circumference of a circle. You will now look at using the formula to find the area of one.
To find the area of a circle you need to use the formula:
Area of a circle = pi × radius2
This can also be written as:
A = πr2
where:
A = area
π = pi
r = radius
r2 means r squared.
Hint: Remember that when you square a number you simply multiply it by itself, radius2 is therefore simply radius × radius.
Let’s look at an example.
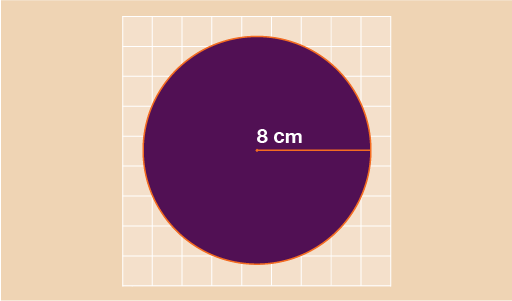
In the circle above you can see that the radius is 8 cm. For these tasks we will use the figure of 3.142 for π.
To find the area of the circle we need to do:
A = πr2
A = 3.142 × 8 × 8
A = 201.088 cm2
Before you try some on your own, let’s take a look at one further example.
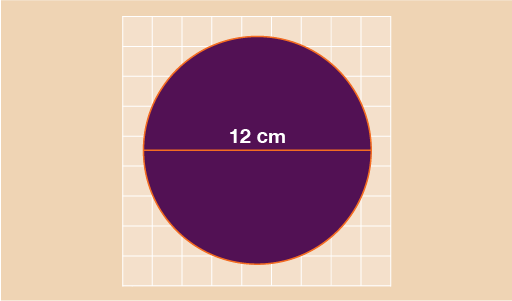
This circle has a diameter of 12 cm. In order to find the area, you first need to find the radius. Remember that the radius is simply half of the diameter and so in this example radius = 12 ÷ 2 = 6 cm.
We can now use:
A = πr2
A = 3.142 × 6 × 6
A = 113.112 cm2
Try a couple of examples for yourself before moving on to the next part of this section.
Activity 6: Finding the area of a circle
Find the area of the circle shown below. Give your answer to one decimal place.
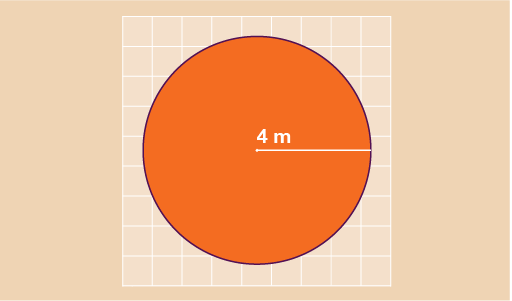
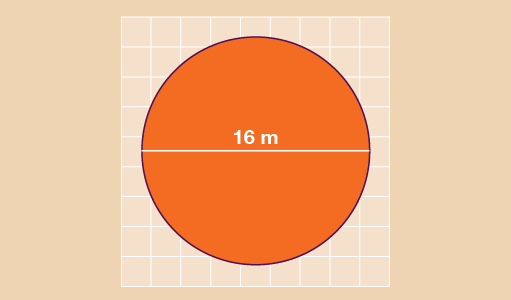
Find the area of the circle shown below. Give your answer to 1 decimal place.
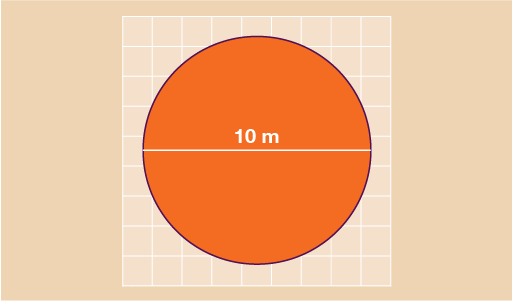
You are designing a mural for a local school and need to decide how much paint you need. The main part of the mural is a circle with a diameter of 10 m as shown below. Each tin of paint will cover an area of 5 m2. You will need to use two coats of paint. How many tins of paint should you buy?
Answer
- To find the area of the circle you need to do:
- A = πr2
- A = 3.142 × 4 × 4
- A = 50.272 m2
- A = 50.3 m2 to 1 d. p.
- You need to find the radius of the circle first. Since the diameter of the circle is 16 cm, the radius is 16 cm ÷ 2 = 8 cm. Now you can find the area:
- A = πr2
- A = 3.142 × 8 × 8
- A = 201.088 cm2
- A = 201.1 cm2 to one d.p.
- You need to find the area of the circle first. Since the diameter of the circle is 10 m, the radius is 10 m ÷ 2 = 5 m.
Now you can find the area of the circle:
- A = πr2
- A = 3.142 × 5 × 5
- A = 78.55 m2
So the area of the circle you need to paint is 78.55 m2
Since you need to give 2 coats of paint, you need to double this number:
- 78.55 × 2 = 157.1 m2
You now need to work out how many tins of paint you need. As one tin of paint covers 5 m2 you need to do:
- 157.1 ÷ 5 = 31.42 tins
Since you must buy whole tins of paint, you will need to buy 32 tins.
You have now learned all you need to know about finding the area of shapes! The last part of this section is on finding the volume of solid shapes – or three-dimensional (3D) shapes.
Summary
In this section you have learned:
that area is the space inside a two-dimensional (2D) shape or space
how to find the area of rectangles, triangles, trapeziums and compound shapes
how to use the formula to find the area of a circle.