3 Deciding what to research
Selecting an appropriate research topic is the first step towards a satisfactory project. For some people, choosing the topic is easy because they have a very specific interest in an area. For example, you might be interested in studying training and development systems in multinational companies (MNCs), or you might have a pressing work issue you want to address, like why the career progression of women in the construction industry is slower than that of men in the same industry. Alternatively, your sponsoring organisation might like you to carry out a specific project that will benefit the organisation itself, for example, it might need a specific HR policy to be developed.
While you may be among those who already have clear ideas, for other learners the process of choosing the research topic can be daunting and frustrating. So how can you generate research ideas? Where should you start? It is easiest to start from your organisational context, if you are currently in employment or if you are volunteering. Is there anything that is bothering you, your colleagues or your department? Is there a HR issue that could be addressed or further developed? Talking about your project with colleagues and family may also help as they may have suggestions that you have not considered.
The following case study describes a process that might help you to identify opportunities in your daily activities that could lead to a suitable topic.
Case study
Lucy works as a HR assistant manager for a large manufacturer of confectionery that operates at a national level. The company has three factories and a head office. While the company has a centralised HR function based at the head office, Lucy is based at one of the factories (the largest of the three) that employs 176 workers. The HR department at the factory comprises three HR experts: the manager and two assistants. Their focus is mainly concerned with the training and development of the on-site staff, with the recruitment of factory workers, grievances, disciplinary and day-to-day HR management. It excludes general issues such as salaries, benefits, pensions, recruitment and development of managerial staff and more centralised aspects that are managed by the HR function at head office level.

For some time, Lucy has received feedback through the appraisal system and exit interviews that shop floor workers are dissatisfied by the lack of progression to supervisory level positions within the company. In fact, the company had no career progression plans nor a structured assessment of training needs for factory workers, who make up the majority of employees. Training was provided on-site by supervisors, managers and HR managers and off-site by external consultants when a specific skill or knowledge was needed. Equally employees could request to attend a course by choosing from a list of courses provided on a yearly basis. However, although the company was keen for employees to attend training courses, these were not systematically recorded on the employee file nor did they fit in a wider career plan.
Lucy is doing a part-time postgraduate diploma in HRM at The Open University and she has to complete a research project in order to gain CIPD membership. She has fully considered this issue and thought that it could become a good project. It did not come to her mind immediately but was the result of talks with her HR colleagues and her partner who helped her to see an opportunity where she could not see it.
Lucy talked to supervisors and factory workers and she analysed the organisational documents (appraisal records and exit interview records). Having searched the literature on blue-collar worker career development and training she compiled a loose structure (semi-structured) for interviews to be conducted with shop floor employees. At the end of her course she submitted a project which included the development of an online programme that managed a record system for each employee. The system brought together all the training courses completed as well as the performance records of each employee. It became much easier for managers and supervisors to identify the training courses attended by each employee as well as future training needs.
When people are employed in a job, or on a placement, and are undertaking research in the employing organisation they can be defined as (insider) practitioner–researchers. While the position of insider brings advantages in terms of knowledge and access to information and resources, there may be political issues to consider in undertaking and writing up the project. For example, a controversial or sensitive issue might emerge in the collection of data and the insider researcher has to consider carefully how to present it in their writing. Furthermore, while the organisation or some of its members may initially be willing to collaborate, resistance to full participation may be experienced during some stages of the project. If you are carrying out research in your own organisation it is therefore important to consider, in addition to its feasibility, any political issues likely to emerge and whether your status may affect the process of undertaking the research (Anderson, 2013).
Another way that can help you to identify a topic of investigation is through reading a HR magazine (such as People Management, Personnel Today or HR Magazine), a journal article or even a newspaper. What topics do they include? Are you interested in any of them? Would the topic appeal to your organisation? Could it be developed into a feasible project?
If you develop an idea, however rudimentary, it is worth writing down the topic and a short sentence that captures some aspects of the topic. For example if the topic is ‘diversity in organisations’, you might want to write a note such as ‘relationship between diversity policy and practices’. From here you can start to develop a map of ideas that will help to identify keywords that can be used to do a more in-depth search of the literature. Figure 2 shows the first step in developing the idea.
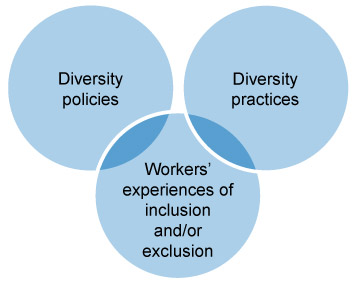
The figure shows three general approaches that you might take in developing a research project on diversity in organisations. You may decide to focus on one of these aspects and you could brainstorm it and add elements such as relationships with the various other aspects, national and organisational context, organisational sector, legislation, and aspects of diversity (e.g. age, gender, sexuality, race, etc.). Obviously this is an example but you can apply this process to any topic.
Activity 2
If you have an idea of a topic for your project, take five minutes to think about the possible perspectives from which it can be investigated. Having done this, take a sheet of paper and write the topic in the middle of the page. Alternatively, if you are still uncertain about the topic you want to investigate, you might want to think about the role of the HR practitioner and the various activities associated with this role. As you consider the various aspects of the role of HR practitioner, you may realise that one of these can become your chosen topic.
Starting from this core idea, now draw a mind map or a spider plan focusing on your chosen topic.
Discussion
Mind mapping gives you a way to illustrate the various elements of an issue or topic and helps to clarify how these elements are linked to each other. A map is a good way to visualise, structure and organise ideas.
Now that you have identified your research topic you can move on to work on the research focus. Activity 3 will help you with this.
Activity 3
Develop a research statement of approximately 600 words explaining your chosen topic, the research problem and how you are thinking of investigating it.
You could start by using the mind map you developed in Activity 2. If you wished, you could do some online research around your topic to get a clearer focus on your own project. You might also read a few sources such as newspaper or magazine articles that are particularly relevant to your topic. These sources may yield some additional aspects for you to investigate. If your topic has been widely researched, try not to feel overwhelmed by the amount of existing information. Focus on one or two articles that appear more closely related to your topic and try to identify the specific area you want to focus on.
Once you have researched the topic, consider the research problem and how this can be investigated. Would you need to interview specific people? Would a questionnaire be more appropriate if you need to access a large number of individuals? Would you need to observe work practices in a specific organisation?
Your statement is a draft research proposal and should include:
- an overview of the topic area with an explanation of why you think this needs to be researched
- the focus of the research and the problem it addresses (and possibly the research questions if you have a clear idea of them at this stage, however, this is not essential if you are still developing the focus of your research)
- how the problem can be investigated (i.e. questionnaire, interviews, secondary data).
You may want to show this proposal to colleagues and other contacts who may be interested in order to gain their feedback about the focus and feasibility.
There is no feedback on this activity.
The next section discusses the ethical issues that need to be considered when doing a research project.