5.1.11 Physical topology
A network topology is a kind of map that identifies various elements of a computer network. A network is represented by two topology types: physical and logical.
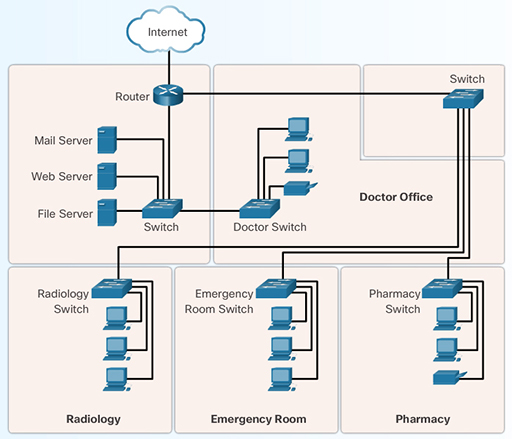
The physical topology displays the layout and location of all of the devices that comprise the network. The physical topology describes how devices are actually interconnected with wires and cables, as shown in Figure 6.
This physical topology will change when mobile devices are incorporated into the network. Mobile devices require connectivity, regardless of their location, for access, monitoring, and control. Some sensors may be located beyond the range of traditional wireless solutions and it may be too expensive to connect them with data cabling. Cellular connections may be required to provide the necessary data links to controllers, central data storage or processing equipment.
The mobile devices must be represented in the physical topology. For wireless connectivity, an inspection, called a site survey, should be done to determine a basic, physical topology.
These are some considerations when determining a physical topology:
- the location of user computers
- the position of network equipment, such as switches, routers, and wireless access points
- the position of controllers and servers
- the position of sensors and actuators
- the potential for future network growth.
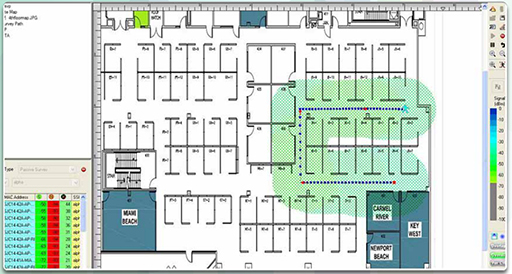
Wireless access points must be strategically placed throughout the hospital to relay data. A wireless survey shows where the wireless access points can be located and the strength of the wireless signals, as shown in Figure 8. Wireless access points may be moved to distribute coverage, or additional access points may be installed where needed. The physical topology must be updated to reflect any devices that have been relocated or added.