5 Volume
Volume is the measure of the amount of space inside of a solid (3D) object. The volume of a cube or cuboid is measured by multiplying length by width by height. It is always measured in cubic units, such as mm3, cm3, m3, etc.
Example: Volume of a cuboid
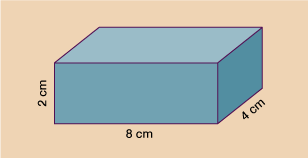
What is the volume of a box with a length of 8 cm, a width of 4 cm and a height of 2 cm?
Method
The volume is:
8 cm × 4 cm × 2 cm
You can also write this as:
32 cm (8 cm × 4 cm) × 2 cm = 64 cm3
Watch the following clip for some more examples:
Now try the following activity.
Activity 11: Calculating volume
- Calculate the volumes of the following:
Hint: As with perimeter and area, you may need to convert to make the units the same.
| Length | Width | Height | Volume |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 m | 2 m | 3 m | |
| 10 mm | 10 mm | 10 mm | |
| 36 mm | 2 cm | 4 cm | |
| 9 m | 2 m | 180 cm |
- A children’s sandpit is 1 m wide and 1.5 m long. What volume of sand would be needed to fill the sandpit to a depth of 10 cm? (Note that depth is the same as height but measured in a downward direction.)
- David has built a log store that measures 2 m × 1 m × 1 m. He wants to order some logs ready for the winter. The local supplier only delivers logs in 1.5 m3 loads. Will David’s store be big enough to hold one load?
Answer
- The answer is as follows:
| Length | Width | Height | Volume |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 m | 2 m | 3 m | 36 m3 |
| 10 mm | 10 mm | 10 mm | 1 000 mm3 |
| 36 mm (convert to 3.6 cm) | 2 cm | 4 cm | 28.8 cm3 |
| 9 m | 2 m | 180 cm (convert to 1.8 m) | 32.4 m3 |
- First you need to convert 10 cm to metres – it’s 0.1 m. Then you can calculate area:
- 1 m × 1.5 m × 0.1 m = 0.15 m3
- The volume of David’s store is 2 m × 1 m × 1 m = 2 m3, so it will be big enough to hold one load of the logs.
Summary
In this section you have calculated the volume of cubes and cuboids.