3.8. Roles and responsibilities
School managers have a range of responsibilities to ensure the school community is inclusive for all their learners and families. Some examples are below.
- Ensure a culture of ongoing self-evaluation, evaluate evidence from across the whole school and use this to plan change and further improve.
- Ensure all duties and responsibilities are carried out as required.
- Ensure all planning and implementation takes cognisance of national and local drivers.
HGIOS 4 identifies 5 quality indicators for leadership and management which can help evaluate specific areas of focus.
1.1 Self-evaluation for self-improvement
1.2 Leadership of learning
1.3 Leadership of change
1.4 Leadership and management of staff
1.5 Management of resources to promote equity
Classroom teachers
Support for all learners begins within the classroom and is provided by the classroom teacher, who holds the main responsibility for nurturing, educating and meeting the needs of all pupils in their class. They work in partnership with support staff to ensure early identification of pupils’ additional support needs and to plan, deliver and review curriculum programmes.
Role of the Support for Learning teacher (SfL teacher)
The Support for Learning teacher works in partnership with appropriate practitioners and parents to meet the additional support needs of children and young people within their local authority staged level of intervention process. They assist class teachers and school management to ensure that children who have additional needs have those needs identified and met within Curriculum for Excellence.
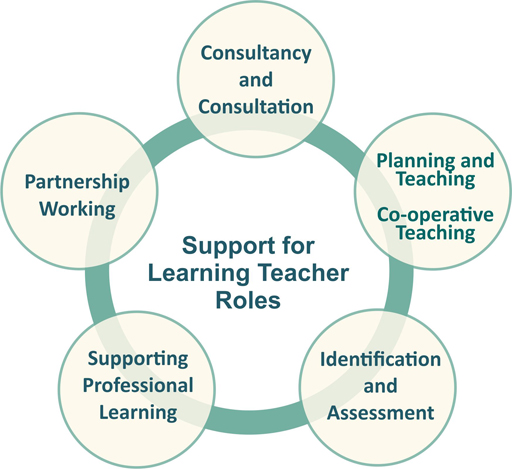
Support should be delivered through the five well established roles of the Support for Learning teacher. These 5 roles are all complementary, and no one role should be carried out in isolation. Figure 21 provides an overview of these roles.
- Consultancy/consultation
Consultancy can take place in many forms, from simply giving advice to working collaboratively with individuals or departments. Effective learning and teaching strategies may be discussed and developed and suitable resources identified and made available. It is important to discuss and reach conclusions on issues such as meeting the needs of learners with a variety of different needs, not just concerning literacy, but also behavioural issues with implications for classroom management, motivation etc. There is likely also to be help regarding the most appropriate resources for the identified needs or individual learners.
- Planning learning and teaching; including co-operative teaching with class teachers
SfL teachers may teach alongside class teachers in the classroom. Clear aims should be set out beforehand and subsequently reviewed. This helps provide direct support, as well as monitoring the progress of all pupils in class, developing classroom strategies with the subject teacher and assisting in recording and assessment.
Sometimes it is helpful for pupils, individually or in small groups, to work out of class with a member of SfL staff. This can aid the ongoing process of dynamic assessment and establishing what is likely to work best. Blocks of support may be given to larger groups of pupils to focus on development of specific skills. Though this works in primary schools, it is particularly important in secondary schools in preparing learners for important exams and applying for further and higher education. SfL will be involved in planning and delivering specialised/focused programmes.
- Identification and assessment
Working with colleagues to ensure the early identification of pupils additional support needs. SfL teachers will be involved with observations, formative and summative assessments, screening and dissemination/feedback to parents/carers/staff/multi agency colleagues.
The SfL teacher/department holds information on individual pupils and is involved in further ongoing assessment and support when this is appropriate. The SfL teacher has some delegated responsibilities for ensuring that information on individual pupils is appropriately disseminated both in school and to external agencies and parents
- Partnership with specialist services
Partnership working is very important to ensure an holistic approach is taken in gathering information and placing the child/young person at the centre. Support teachers will be in regular contact with colleagues in schools/educational services and multi-agency colleagues e.g. health, social work and voluntary agencies.
- Contributing and supporting professional development
The SfL teacher/department contributes to staff development in a variety of ways through:
- Sharing of insight, experience and resources
- Presentation of in-service sessions: for example twilight collegiate sessions
- Offering guidance on accessible resources/materials, curriculum, equipment and approaches
- Sharing effective strategies, disseminating information from courses attended.
- Disseminating information to staff on local authority procedures, legislation and guidelines.
Activity 26 Reflections on your practice
Complete the table in your Reflective Log. Consider how you are able to engage with the 5 roles.
Support staff
Support staff play a key role within the school community to ensure that information is communicated to colleagues about effective practice to support learners with additional support needs and about individual learners who staff work with. This may take the form of a pupil profile or information within SEEMiS. Further information on the pupil profile can be found in Section 2.4.
All staff represent the school and therefore the local authority when they meet with parents and learners.
There are a range of roles within support teams, for example, support assistants, support for learning teachers, additional support teachers or Deputy Heads for support. Irrespective of their role, all educational practitioners need to have good interpersonal skills in order to support effective communication within their school community on the identification, support, monitoring and progress of learners. The essential skills include:
- Empathy
- Effective people skills
- Ability to listen
- Following up and communicating on actions
Activity 27 Reflective practice task
In your Reflective Log, consider how you have communicated the process of identification to:
- Parents
- Learners
- Colleagues
Consider and reflect:
- How did I do it?
- What made the difference?
- How can I improve the experience for all involved?
3.7. Transitions