1.2.5 Blood pressure (BP)
Blood pressure (BP) refers to how hard the blood is pushing on the major blood vessels as it is pumped around the body by the heart. It is measured in millimetres (mm) of mercury (a liquid silver metal, which has the chemical symbol Hg), so blood pressure measurements are expressed as a number followed by mmHg. The technique of measuring blood pressure (Figure 1.6) was described first in the Antenatal Care Module, Study Session 9, and you have learned it in your practical skills training. Figure 1.7 reminds you how to measure the blood pressure at two points in time: when the heart contracts and when it relaxes.
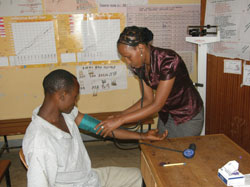
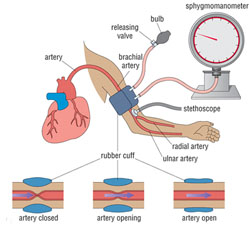
A blood pressure measurement is two numbers written one above the other. The top number tells you the systolic pressure, which is the pressure at the moment the heart beats and pushes blood into the body. The bottom number tells you the diastolic pressure when the heart relaxes between each beat so it can refill with blood. Healthy blood pressure stays at or above 90/60 mmHg, but should not reach as high as 140/90 mmHg.
1.2.4 The pulse
