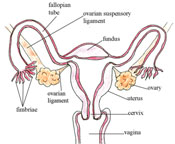
3.6 Cervical cancer
Cervical cancer refers to cancer cells growing in the tissues of the cervix – the muscular organ connecting the uterus and the vagina (Figure 3.5). Most cases of cervical cancer are caused by sexually transmitted infection with the human papilloma virus (HPV).
In low- and middle-income countries, cervical cancer is the most common female cancer and one of the leading causes of death amongst women. In Ethiopia, it is believed from hospital reports that cervical cancer is the most common of all cancers. It is usually a slow-growing cancer that may not produce symptoms in its early stages. If the cancer is advanced, it may produce symptoms including an offensive discharge and bleeding from the vagina, and pain during sexual intercourse. You should encourage any woman with these symptoms to seek urgent medical attention.
3.5.2 Breast cancer treatment