1.2.1 Deforestation
One particular problem caused by over-exploitation of natural resources is deforestation, which occurs when forest areas are cleared and the trees are not replanted or allowed to regrow. In Ethiopia, clearing land for agriculture to meet the food needs of the growing population and the demand for fuel and construction materials has resulted in a steady loss of forest area, which is still continuing as you can see from Figure 1.3.
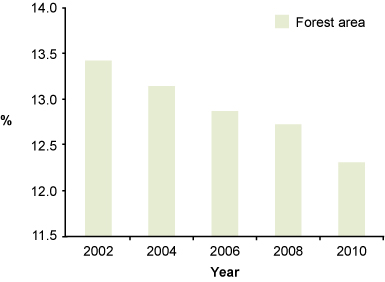
The loss of forest has several undesirable consequences. Forests are home to many different types of trees, as well as other plants, and a wide range of animals from insects to birds and mammals. The conversion of forests to agriculture greatly reduces biodiversity, which is a measure of the variety of living organisms (all life forms). Biodiversity is important for humans because we use other living organisms to provide several essentials:
- Food: we use plants and animals such as fish, goats, wheat, rice and maize as sources of food.
- Medicines: many traditional medicines are made from plants and animals and new medicines are developed from them.
- Ecological services: living organisms, especially plants and micro-organisms, play an important role in processes that maintain our lives and environment such as providing oxygen, cleaning the air, purifying water, breaking down wastes and controlling erosion.
Deforestation is a significant contributory cause of soil erosion. Once the trees and undergrowth are removed, the underlying ground is exposed. Without the intercepting effect of the vegetation and the tree roots binding the soil together, the soil is more likely to be washed away when it rains. Loss of forests also has a significant impact on water supply. Tree roots reach deep into the soil and create spaces between the particles which increases soil permeability, allowing rainwater to soak in and replenish groundwater. (Permeability means the ease with which water moves through soil or rock.)
1.2 Use of natural resources
