5.5.3 Biogas latrines
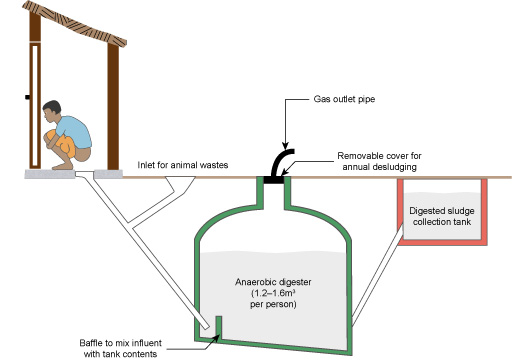
In a biogas latrine or bio-latrine (Figure 5.13), the waste enters an airtight tank situated underground, and undergoes anaerobic digestion, resulting in the production of biogas and digested sludge. Biogas is a clean and convenient fuel that contains about 60% methane. Anaerobic digestion is the process whereby bacteria and other micro-organisms break down (decompose) organic material in the absence of air, yielding biogas. The digested sludge collects in a separate tank and can be used as a soil fertiliser.
Biogas can be used for cooking and lighting, refrigeration, engine operation and electricity generation. Animal wastes can also be added to the digester. Being a relatively expensive system, this has been applied in Ethiopia only at public latrines (Figure 5.14) and institutions such as schools, colleges, universities, hotels and prisons, where large numbers of people use the latrine.

5.5.2 Urine-diverting latrine