5 TESS-India pedagogy
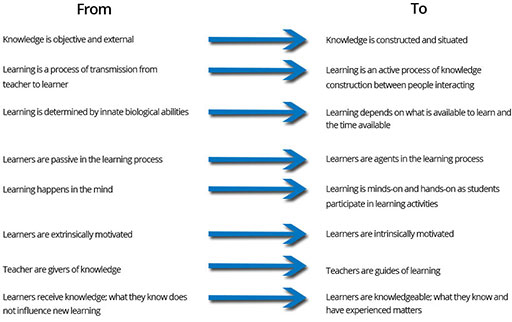
The TESS-India OER are designed to help move teacher educators and teachers towards deeper engagement with the participatory ‘learner-centred’ pedagogy articulated in Indian policy documents (NCF 2005, NCFTE 2009). Through engaging in the OER activities, teachers are encouraged to move away from practices based on traditional assumptions about learning and learners, which are teacher-centred and hierarchical. Instead, they are supported in moving towards understandings of effective teaching and learning that are underpinned by research. This learning movement is described in the table below.
Reflection point
Think about three or four teachers that you know. Where would you place them on each of the dimensions above, on the left or the right? Where are their views on learning mainly located?
How does this link to your response to Activity 1.1?
The pedagogy in the TESS-India Teacher Development OER focuses on modelling practice for teachers that consistently conceptualises students as:
- knowledgeable
- constructors of meaning and problem solvers
- self-regulated and self-directed
- intrinsically motivated if learning activities have personal meaning and cultural authenticity.
The pedagogy of the TESS-India OER challenges a ‘teacher-centred’, lecture-driven approach, and positions learners in a way that is congruent with the policy that you encountered earlier this week. But what does this pedagogy look like in the classroom? You will explore this in Activity 1.6.
Activity 1.6: Implications for teachers
- Listen to Professor Patricia Murphy from The Open University [Tip: hold Ctrl and click a link to open it in a new tab. (Hide tip)] talk about the thinking behind India’s NCF (2005) and how it informed the development of TESS-India’s OER.
- As you listen, note down the implications for classroom practice of the learner-centred pedagogy. For example, if it is important to recognise students’ prior knowledge and experience, what can teachers do to understand what their students know? And what kinds of activities can teachers carry out to enable students to interact in order to actively construct knowledge?
4 Introducing TESS-India