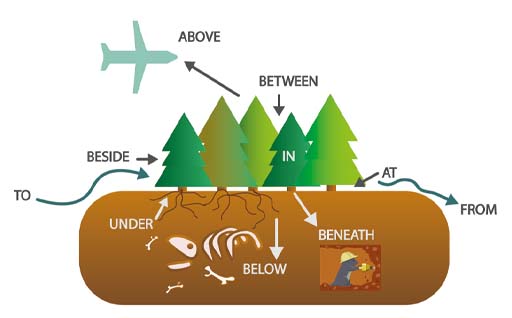
3.3 Prepositions
Prepositions are words that indicate location or movement in physical space, mental space, or time. In other words, they tell you where (or when) something is, was, or will be. Examples include to, from, of, for, on, off, in, out, over, under, above, below, around, in front of, behind, before, after, inside, outside.
Activity 6 Add the prepositions
Look at the sentences below. What prepositions from the list above would fill the gaps? The correct number of letters is given.
Discussion
1. Mary met John in Paris on Tuesday.
2. On Tuesday we travelled to Paris.
3. Mary drove to Paris with John.
4. John arrived at the Louvre before Mary.
5. At 5pm precisely John greeted Mary with a friendly smile at the Louvre.
6. In an instant the meeting changed from business to celebration.
The parts of these sentences that begin with a preposition are examples of what we call prepositional phrases. They usually act as a single unit and we can move them around in the sentences quite a bit:
On Tuesday Mary met John in Paris
In Paris Mary met John on Tuesday
Mary met John on Tuesday in Paris