3 Understanding numbers
As part of learning about maths, you need to understand how numbers work – both whole numbers and decimals.
Every number that we see around us is made up of a series of digits, such as 1302 (one thousand, three hundred and two). The value that each digit has depends not only on what that digit is, but also on its place, or position, in a number. This allows you to represent any number that you want by using only 10 digits (0, 1, 2, 3 etc.).
Each place in a number has a value of ten times the place to its right, starting with ones – or called more properly units – then tens, hundreds, thousands and so on. So in 1302, the 2 is in the units place, the 0 is in the tens place, the 3 is in the hundreds place and the 1 is in the thousands place. This means that the 3 has a value of 300 and the 1 has a value of 1000.
If you now rearrange the digits in your first number they will have different values and you’ll have a new number. So, 3120 has all the same digits but now the 3 is 3000, rather than 300 as it has moved one place to the left.
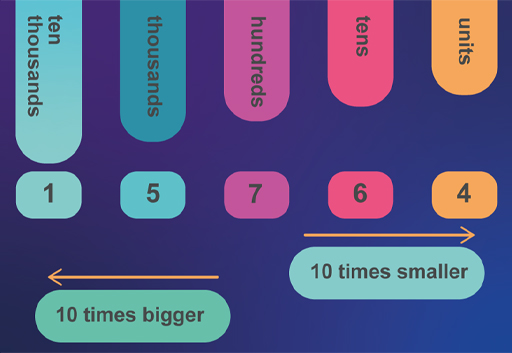
Now have a look at another example in Figure 8.
You can see in Figure 8 that the following is true:
- 1 is in the ten thousands place
- 5 is in the thousands place
- 7 is in the hundreds place
- 6 is in the tens place
- 4 is in the units place.
… and the number is 15 764, which is spoken as ‘fifteen thousand, seven hundred and sixty-four’.
Using this system, you can write and understand any whole number, but as you are probably aware numbers are not limited to only whole numbers. You also need ways to represent parts of whole numbers. The two ways that you do this are by using either decimal numbers, like 3.25, or fractions, such as .
You’ll start with a look at decimal numbers, and then in the coming weeks you will learn about fractions.