2 Multiplying fractions
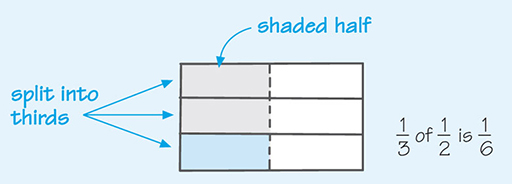
To help visualise multiplying fractions, take a piece of paper again. To find out what one-third of one-half is, fold your piece of paper in half along the long side and shade one half of the paper. Then, fold it into thirds along the short side. The paper is now split into six equal pieces, or sixths. If you look at the shaded half, you can see that one out of three parts of this portion represents one out of six parts of the entire piece of paper, as shown in Figure 1. This is the same as saying that it is one-third of a half.
Mathematically, this is written as .
If you look at this carefully, you should be able to see that to multiply these two fractions, the numerators were multiplied together, and the denominators were multiplied together. This is the way that all fractions are multiplied. You must just remember to show any answer in its simplest form.
It is often easier to cancel or simplify before multiplying, as this can give you easier numbers to deal with. For example, looking at , multiplying the numerators and then the denominators together gives , but you can cancel the 2s using division:
This calculation is equivalent to cancelling at the start of the calculation:
Try this for yourself in the next activity.
Activity 3 Multiplying fractions
Carry out the following examples, showing your final answers in the simplest form.
- a.
Hint: remember to multiple the numerators and then the denominators together.
Answer
a.Cancel by dividing by 3.
- b.
Answer
b.Cancel by dividing by 2.
- c.
Answer
c.Cancel by dividing by 5 and 12.
You will remember from Week 3 that you will also come across mixed numbers, which are a combination of whole numbers and proper fractions. In the next section you will look at calculations involving mixed numbers.