2.2 Sodium chloride
Sodium chloride is an ionic compound, and this tells you when forming bonds electron loss and gain to form ions must be involved.
Sodium has the electronic configuration, 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 (or [Ne] 3s1) so it has one valence electron. It can acquire a filled outer shell by transferring its outer electron to the chlorine atoms.
And you know, adding one electron to a chlorine atom will give it a noble gas configuration.
How will the charges on sodium and chlorine be changed by this transfer of an electron?
Remember electrons are negatively charged, so if sodium is losing an electron it must become a positively charged ion – it forms a cation. Likewise when chlorine gains an electron it will become negatively charged – an anion.
So the transfer of the electron to chlorine in NaCl produces ions, each of which can exist independently of any one partner. As they are oppositely charged there will be an attraction between them – this attraction is the ionic bond.
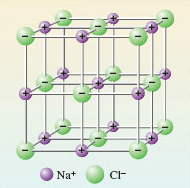
In sodium chloride, each ion is surrounded by as many ions of opposite charge as space allows. In this case the number is six (Figure 1).
It is worth making the point here that although this is the way ionic bonding is usually taught, and has stood the test of time, it is rather an unrealistic situation in practice, rather is a convenient ‘thought experiment’.
Yes – you can pass chlorine gas over sodium and a reaction will take place to form sodium chloride. But generally speaking you don’t get sodium atoms and chlorine atoms interacting together and electron transfer occurring as described above. A much more likely process is for ionic compounds form from solutions in water in which the ions are already present and crystallise out of solution when water is evaporated.
However – this apart – the basic definition of the ionic bond still stands – that is the electrostatic attraction between cations and anions.