6.1 Different generations of cephalosporins
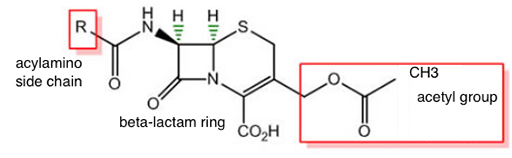
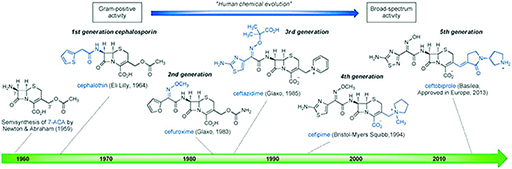
There are five generations of cephalosporins. Figure 8 shows how two chemical groups of 7-ACA, the acetyl group and the acylamino side chain can be modified, leaving the ‘nucleus’ intact. Do not worry if you are not familiar with these chemical structures. For this course you should just be aware that these modifications give rise to different generations of cephalosporins with a different spectrum of activity. If you would like to know more about chemical reactions you might like to try our free OpenLearn course Discovering chemistry [Tip: hold Ctrl and click a link to open it in a new tab. (Hide tip)] . For examples of each generation, see Figure 9.
Each successive cephalosporin generation has improvements in the spectrum of activity and in some pharmacological properties. This greatly expands the clinical uses of these drugs. The later generations are sometimes called ‘extended spectrum cephalosporins’ (ESCs).
In Activity 6, you can compare the characteristics of different generations of cephalosporins.
Activity 6 Characteristics of cephalosporin generations
Table 1 below summarises the characteristics of different cephalosporin generations.
| Cephalosporin generation | Activity against: | Resistance to: | Examples | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gram-positive | Gram-negative | MRSA | ß-lactamase | ESBLs | ||
| 1 | ++++ | + | no | + | no | cephalothin cefazolin |
| 2 | +++ | ++ | no | ++ | no | cefamandole cefaclor |
| 3 | ++ | +++ | no | ++ | no | cefixime ceftriaxone |
| 4 | ++++ | ++++ | no | +++ | no | cefepime cefclidine |
| 5 | ++++ | ++++ | yes | +++ | no | ceftobiprole |
Key: + = trace amount; ++ = small amount; +++ = moderate amount; ++++ = large amount.
Review the table and then answer the following questions.
- Which generation has the lowest activity against Gram-negative bacteria and which has the highest?
- With each successive generation, what do you notice about the activity against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria?
- Which generation(s) have the greatest resistance to ß-lactamases?
- Are any cephalosporins resistant to ESBLs?
- Which cephalosporin has activity against MRSA?
Answer
- The first-generation drugs have the lowest activity against Gram-negative bacteria; the fourth and fifth generations have the greatest.
- The first-generation cephalosporins had good activity against Gram-positive bacteria but poor activity against Gram-negative bacteria. Activity against Gram-negative bacteria improved with second and third generation drugs, but at the expense of activity against Gram-positive bacteria. The last two generations of cephalosporins have good activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
- The fourth and fifth generations
- No. Resistance to ESBLs, particularly those produced by Gram-negative bacteria, is becoming a serious problem.
- Fifth generation cephalosporins, like ceftobiprole, are active against MRSA.
The chemical evolution of cephalosporin C via 7-ACA into over 30 new broad-spectrum antibiotics was a breakthrough in the fight against antibiotic resistance. Unfortunately, the widespread practice of using cephalosporins for empiric treatment, that is treatment without a definitive diagnosis, may have selected for multi-drug-resistant bacteria and encouraged the spread of resistance (Clegg, 2015).
The need for new antibiotics is urgent and, as you will see in the final section this week, scientists are looking in some unlikely places for them.