3.5.1 Roundworms, hookworms and anaemia
Pathogenic soil-transmitted roundworms (or nematodes) are transmitted harmlessly from person to person via worm eggs shed into the soil in human faeces. At least 1700 million (or 1.7 billion) people worldwide have these worms in their intestines. Children in heavily infected communities may harbour more than 1000 worms, causing diarrhoea, discomfort and restricting the child’s growth.
ITQ 3.5.1
-
Can you suggest how children get worm eggs onto their hands and transfer them from hand to mouth?
-
Particles of dirt contaminated with worm eggs stick to the hands when children play or work on soil; if hands aren’t washed before eating, the eggs can easily transfer to the child’s mouth.
Lack of water and soap for handwashing, as well as lack of sanitation, are major contributory factors in hand-to-mouth transmission of all pathogens, not only worms.
Hookworms (Figure 5) are soil-transmitted roundworms measuring 5–10 mm (millimetres), which hook onto the inner wall of the human gut and suck blood from the surrounding blood vessels. Over 400 million people are infected with hookworms and as a result suffer a type of anaemia [an-ee-mee-ah] due to loss of red blood cells. Anaemia caused by hookworms contributes to stunting in children (being short for their age) and wasting (being underweight for their height). Hookworms also present a risk to pregnant women and their unborn or newborn babies due to the adverse effects of maternal anaemia.
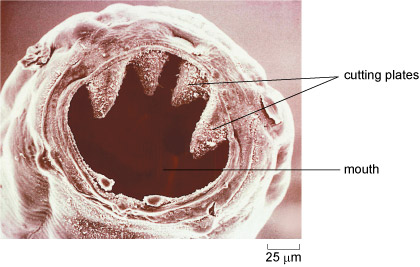
The scale bar in the bottom right corner of Figure 5 gives a measurement in micrometres (µm); one micrometre is one-thousandth of a millimetre (mm) and one-millionth of a metre (m).
