3 Perfectionism: a double-edged sword?
In a survey of the general population in 2009, 53% of people claimed they were perfectionistic at work, 36% were perfectionistic in bodily hygiene and 18% were perfectionistic in sport (Stoeber and Stoeber, 2009). Perfectionism is a personality factor that is consistently associated with burnout because of the relentlessly high standards that people apply to themselves. You may even recognise this characteristic in yourself.

The double-edged sword of perfectionism is illustrated by this quote:
That’s just how you are as a perfectionist, you sacrifice. I sacrificed marriage on it, I sacrificed everything on it … I think [as a performer] I have benefited by being a perfectionist. As a person I probably haven’t.
Perfectionism can be a very positive characteristic helping people excel with high standards, but when accompanied by constant self-critical evaluation it also creates ongoing stress and anxiety. To explain this further look at Figure 5 which demonstrates six characteristic conditions of perfectionism.
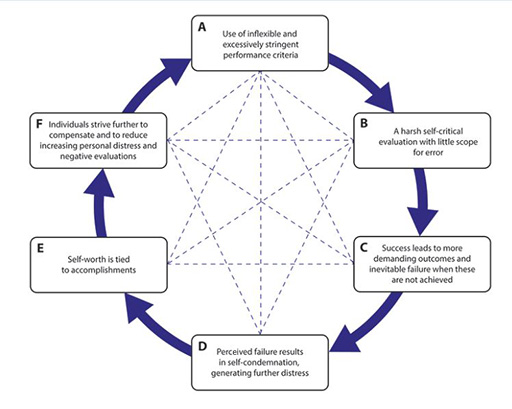
By following the lettered boxes around clockwise from A–F you can see the vicious cycle that perfectionists may experience. The words in the boxes which describe thoughts and behaviours are not always followed in a neat progression. In fact, the dashed lines between boxes indicate complex interactions between them all.
Notice how boxes A, B and F are likely to create a potent drive to train, linking to an overtraining or motivation perspective of burnout; in contrast, items C, D and E suggest associated stress and anxiety, connecting to a stress or overtraining perspective of burnout. Those using a social perspective of burnout would argue that the structure and organisation of sport itself, with constant comparisons with others, creates considerable stress and risks for perfectionists.
You have already seen how perfectionism effected Pendleton’s training experiences but now in the next section you will see a vivid example of a rugby player talking about it.
