2.2 The link between energy and biofuels
You may be wondering why there is this emphasis on the electromagnetic spectrum and light absorption by plants in a unit on biofuels. The sugars that the plants produce from carbon dioxide and water are a concentrated form of energy. Energy cannot be created - it can only be converted from one form to another. The energy in sugars comes from the energy in visible light - sunlight. The plant uses the sugars it produces to form other compounds within its tissues and it is these compounds that can be used as biofuels. Box 3 provides describes in more detail the process of photosynthesis.
Box 3 The reactions involved in photosynthesis
Question 13
From what you have learnt so far, where in the plants cells does photosynthesis take place?
Answer
In the chloroplasts.
The absorption of light takes place within specialised membranes within the chloroplasts called the thylakoid membranes (see Figure 6). In order to pack more closely together the thylakoid membranes can form flattened stacks called grana (singular granum).
The reactions of photosynthesis take place in two phases; the absorption of light takes place in the first phase and the second phase occurs in the watery fluid, the stroma, which surrounds the thylakoid membranes. The chloroplast itself is bounded by two membranes that are situated very close together and called the chloroplast envelope (Figure 6).

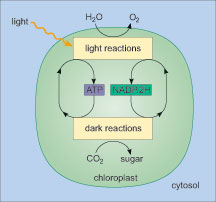
Photosynthesis can be summarised in the simple word equation:
water + carbon dioxide → sugar + oxygen
But this hides the fact that the process consists of two main stages: the so-called 'light reactions' and the 'light independent or dark reactions'.
In the series of very complicated light reactions the energy from sunlight is used to produce two main compounds ATP (which stands for adenosine triphosphate) and NADP.2H (a complicated chemical called nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide). (Don't worry about the names of these two compounds; they are always referred to by their initials.) ATP and NADP.2H are used to convert carbon dioxide, via a complex series of reactions, to sugars - the end point of photosynthesis; these reactions are the dark reactions which take place in the stroma.
Question 14
Why do you think the dark reactions are so called?
Answer
Because the plant does not need the presence of light for these reactions to occur, hence their alternative name - light independent reactions.
Question 15
How does carbon dioxide enter the plant?
Answer
Through small pores called stomata on the leaf surfaces.
The carbon dioxide gas moves (the scientific term for random gas movement is 'diffuses') from a stoma to a chloroplast. There, in a series of reactions that use ATP and NADP.2H, the carbon dioxide binds to a protein called Rubisco (ribulose 1, 5 bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase) and eventually sugar is produced. Different plants will produce different kinds of sugar but most commonly it is glucose. These processes are summarised in Figure 7. The sugar can then be moved throughout the plant to wherever it is required.
It is worth noting that, as photosynthesis is such a widespread process and Rubisco is so central to it, the amount of Rubisco present in plants worldwide has been estimated to be 25% of all protein globally. You shouldn't have any doubts now as to the importance of the photosynthetic process!
