Gold: More than decoration
In ancient Rome tiny particles of gold called nanoparticles were used to stain glass for decorative purposes. In recent years, however, they have started to find applications in medicine; finding uses in tissue imaging, as cancer treatments, in certain types of pregnancy tests and as a means to help deliver drugs to specific parts of the body.
Introducing gold nanoparticles
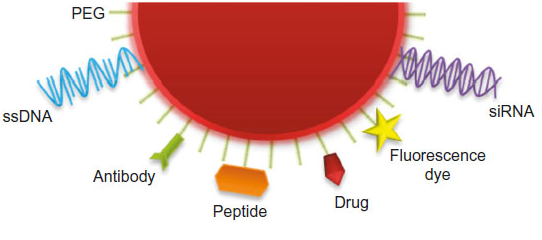 Figure 1: Gold Nanoparticles loaded with a number of moieties, which allows them to act as therapeutic agents, as molecular sensors for diagnostics or as a vehicle for delivering other effective therapeutics and imaging agents to specific locations.
Gold nanoparticles are tiny particles of gold which can be small as 2 nm in diameter. Because of their small size, they have a large surface area and physical and chemical properties which can easily be manipulated. The unique properties of the gold surface mean we can attach different therapeutic molecules (such as drugs, DNA and antibodies) to their surface. As gold nanoparticles can bear a high drug load, this makes them ideal carriers for multiple therapeutic agents (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Gold Nanoparticles loaded with a number of moieties, which allows them to act as therapeutic agents, as molecular sensors for diagnostics or as a vehicle for delivering other effective therapeutics and imaging agents to specific locations.
Gold nanoparticles are tiny particles of gold which can be small as 2 nm in diameter. Because of their small size, they have a large surface area and physical and chemical properties which can easily be manipulated. The unique properties of the gold surface mean we can attach different therapeutic molecules (such as drugs, DNA and antibodies) to their surface. As gold nanoparticles can bear a high drug load, this makes them ideal carriers for multiple therapeutic agents (Figure 1).
Delivering drugs to the brain
Because of their small size, gold nanoparticles can easily travel into target cells. We can use gold nanoparticles specifically to target cells to treat difficult areas of the body, such as the brain. The brain is a highly controlled and protected organ, since there are substances in the blood that may potentially harm it. It is protected by a controlled environment called the blood brain barrier which determines what can pass from the blood into the brain (Figure 2).
The blood-brain barrier makes the treatment for brain diseases very challenging, as it is difficult for drugs to cross. Attaching drugs to gold nanoparticles provides one way in which we can help them pass through the blood-brain barrier and into the brain.
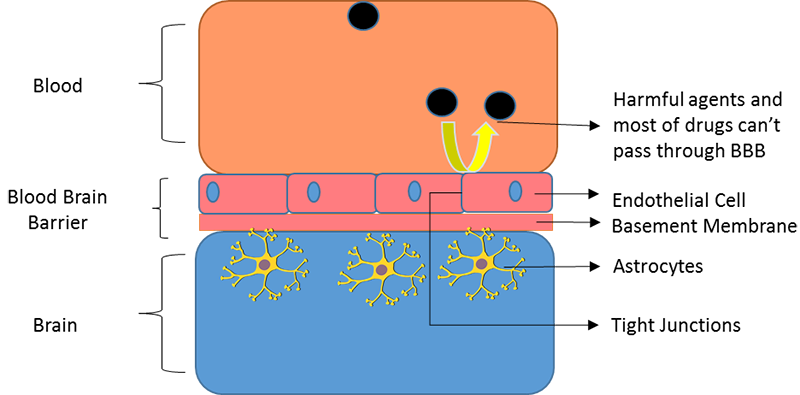 Figure 2: The blood-brain barrier maintaining a controlled environment.
Figure 2: The blood-brain barrier maintaining a controlled environment.
Switching off brain disease
Attachment of DNA, RNA molecules or any other nucleic acid is promising treatment for certain brain diseases. Short-interfering RNA (siRNA) has been proposed for therapeutic uses as they can potentially switch off any gene in the body and thus be useful to treat currently undruggable brain diseases. Coupling nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA to gold nanoparticles does not alter their ability to cross blood-brain barrier and hence gold nanoparticles may provide a useful way of transporting them into the brain.


Rate and Review
Rate this article
Review this article
Log into OpenLearn to leave reviews and join in the conversation.
Article reviews