8.2 Effects of air pollution on the environment
Air pollution is the presence of pollutants in air in quantities that can cause health damage to humans, animals, and plants. When gases such as nitrogen oxides, hydrogen sulphides and sulphur oxides are released into the atmosphere they can dissolve in the water vapour of clouds and fall as rain. The presence of these pollutants acidifies the water and causes acid rain (Figure 8.5).
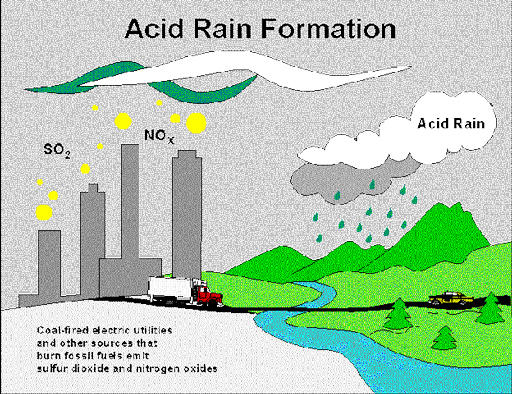
Acid rain usually has a pH of less than 5 and is highly corrosive and damaging, especially to buildings and forests (Figure 8.6). (pH is a measure of acidity and alkalinity on a scale from 0 to 14. pH 7 is neutral; less than 7 is acid; more than 7 is alkaline.)

8.1.3 Effects of persistent pollutants
