2 Lifespan perspective
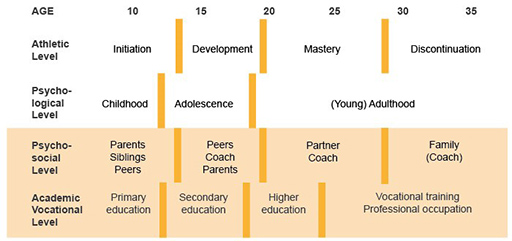
From a holistic viewpoint, it is important to note that the transitions an athlete will face are not exclusively sport related and other transitions will occur across an athlete’s lifespan. As you will see in Wylleman and Lavallee’s (2004) developmental model shown in Figure 1, athletes will typically face normative transitions at an athletic, psychological, psychosocial and academic or vocational level as well. All of these could interact to impact on sports performance.
Briefly study Figure 1, where the orange bars represent the transition boundaries, and then complete the activity that follows where you will explore the elements of this model in more detail.
Although the model indicates that discontinuation on the athletic level occurs just before the age of 30 obviously this is different for different athletes, with many athletes retiring at a much later age and some, particularly those from early specialisation sports such as gymnastics, retiring at an earlier age.
Activity 2 Transitions across the lifespan
Watch the video below which explores the components of Wylleman and Lavallee’s (2004) developmental model. This model allows you to explore the transitions an athlete might experience in different aspects of their lives in order to give you a more rounded or holistic understanding of the individual and their transition experiences. The video talks about the model in relation to a hypothetical case study, Natasha, who is a sprinter.
As you can see the model has 4 ‘levels’ – athletic, psychological, psychosocial and academic/vocational. Within each level there are different normative transitions that an athlete will face that are important to be aware of.
As you watch the video complete the table below by identifying some of the features, potential challenges and impact of the different transitions Natasha experiences.
Transcript: Video 1
Obviously not all athletes will follow this exact path, but it is important to consider the impact these academic and vocational developments can have on the athlete.
| Transition | Features of the transition and potential challenges | Potential impact on sports performance and participation |
|---|---|---|
| Childhood to adolescence | ||
| Adolescence to adulthood | ||
| Primary to secondary education | ||
| Secondary to higher education | ||
| Higher education to vocational training and a professional occupation |
Discussion
Below are some examples of what you might have put in your table after watching the video.
| Transition | Features of the transition and potential challenges | Potential impact on sports performance and participation |
|---|---|---|
| Childhood to adolescence |
|
|
| Adolescence to adulthood |
|
|
| Primary to secondary education |
|
|
| Secondary to higher education |
|
|
| Higher education to vocational training and a professional occupation |
|
|
Through a lifespan perspective an athlete will invariably experience both upward and downward transitions in their performance level, both of which can place demands on the athlete. You will examine each of these in the next section.