3.2 Further exercises
Here are some further exercises to end this section.
Exercise 14
For each of the following functions , evaluate
where is any contour from to .
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
Answer
In each case, is continuous on and has a primitive on , so we can apply the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus to evaluate the integral using any contour from to .
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.A primitive of is
Hence
h.A primitive of is
Hence
i.Let , . Then and are entire (that is, and are differentiable on the whole of ), and and are entire and hence continuous. Then, using Integration by Parts (Theorem 9), we have
Exercise 15
Evaluate the following integrals. (In each case pay special attention to the hypotheses of the theorems you use.)
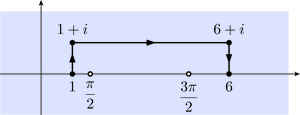
a.,
where is the arc of the circle from to passing through 1.
b., where is as in part (a).
c., where is the unit circle .
d., where is the circle .
(Hint: For part (c), use the identity .)
Answer
a.Let , and . Then is continuous on , is a primitive of on , and is a contour in . Thus, by the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus,
b.Let , and . Then is continuous on , is a primitive of on , and is a contour in . Thus, by the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus,
c.The function
is continuous and has an entire primitive . Thus, by the Closed Contour Theorem,
d.Let , and . Then is continuous on , is a primitive of on , and is a contour in . Thus, by the Closed Contour Theorem,