3 Mind mapping
Mind mapping is a visual tool that helps organise ideas, enhance creativity, and improve memory by connecting related concepts. Many students have heard of mind mapping, but might not know just how useful this tool can be. This is a creative tool that works well with the dyslexic brain (Buzan, 2006).
Mind maps engage with our natural preference for thinking in pictures. They are a visual way of taking or making notes and planning. They show the big picture and how ideas are connected (Myhill, 2022). Mind mapping is a great tool that:
- clarifies thinking and simplifies complex ideas
- encourages creative thinking which produces more ideas
- helps to embed information into your memory
- makes links that trigger recall of complete associated information
- results in an increase in your performance.
Students with dyslexia often prefer non-linear thought and think in multiple directions simultaneously, just like a mind map, starting from central trigger points in key words and key images. A key word is a memory trigger, and when linked to a key image, this stimulates both sides of the brain and involves your senses.
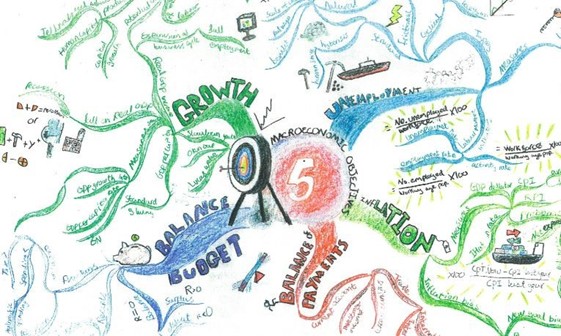
Figure 3 shows an example of a student’s hand-drawn mind map (Myhill, 2022, p. 71):