2.5 Enzymes
Have you ever noticed that if you keep chewing potatoes or rice for a few moments, you get a faintly sweet taste in your mouth? This is the effect of a digestive enzyme in your saliva called salivary amylase. It begins the breakdown of starch to sugars such as glucose which is what tastes sweet.
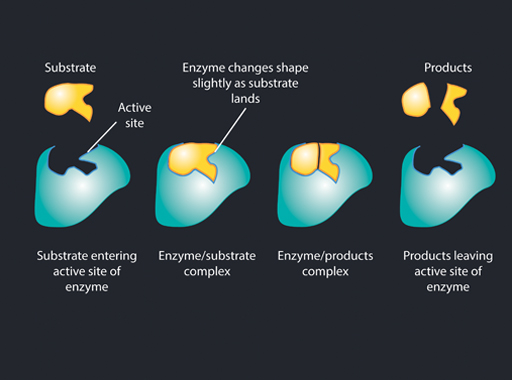
Digestive enzymes, such as amylase, are specially shaped protein molecules that can latch on to a particular type of molecule (carbohydrate, protein or fat) and break it down into smaller molecules (Figure 6). Eventually, the molecules are small enough to be absorbed into the bloodstream through the cells of the intestines.
Each particular type of enzyme usually only works on one type of food molecule. They are named according to the sort of molecule that they affect. For example:
- enzymes that break down proteins are proteases
- those that break down fat are lipases (fats are also called lipids)
- those that break down carbohydrates are amylases (amylose is a component of starch).