2 Area
You need to be able to calculate area if you ever need to order a carpet for your house, buy tiles for a kitchen or bathroom, or calculate how much paint to buy when redecorating.
This patio has paving slabs that are 1 metre square (each side is 1 metre). How many paving slabs are there on the patio?
Area is measured in ‘square’ units. This means that the area is shown as the number of squares that would cover the surface. So if a patio covered with 18 squares that are 1 metre by 1 metre, the area is 18 square metres.
(If you count them, you will find there are 18 squares.)
Smaller areas would be measured in square centimetres. Larger areas can be measured in square kilometres or square miles.
You can work out the area of a rectangle by multiplying the long side by the short side:
width × length = area
The patio is:
6 × 3 = 18 square metres
‘Square metres’ can also be written ‘sq m’ or ‘m2’.
Hint: Always use the same units for both sides. If you need to, convert one side to the same units as the other side.
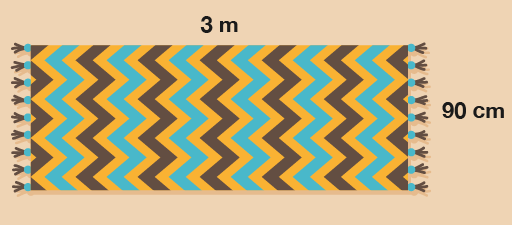
Example: The area of a rug
How much backing fabric is needed for this rug?
Method
To find the answer, you need to work out the width multiplied by the length.
- 90 cm × 3 m = area
First, you need to convert the width to metres so that both sides are in the same units. 90 cm is the same as 0.9 m, so the calculation is:
- 0.9 × 3 = area = 2.7 square metres
Now try the following activity. Remember to check your answers once you have completed the questions.
Activity 4: Finding the area
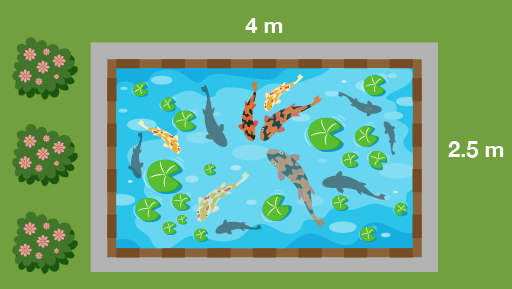
- How much plastic sheeting do you need to cover this pond for the winter?
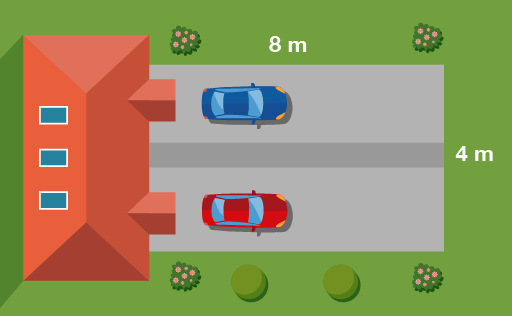
- One bag of gravel will cover half a square metre of ground. How many bags do you need to cover this driveway?
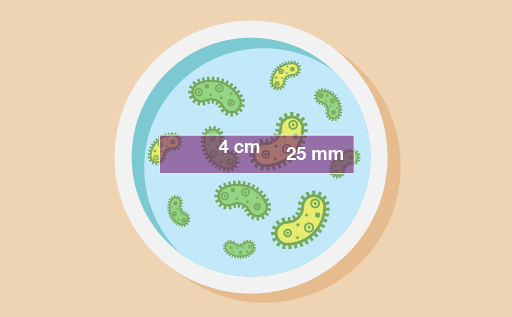
- A biologist is studying yeast growth. In the sample area shown below the biologist found 80 yeast. What would go in the missing spaces in her recording sheet, as marked with a question mark?
| Sample area no. | 21 |
| Date | 17 October |
| Yeast count | 80 |
| Sample dimensions | ? cm × ? cm |
| Sample area | ? cm2 |
| Yeast/cm2 | ? |
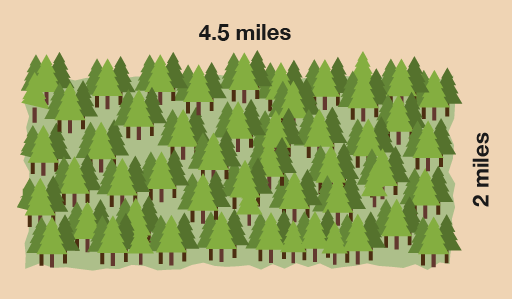
- How large is this area of forestry land?
Answer
The plastic sheeting needs to be:
- 2.5 × 4 = 10 square metres
First you need to work out the area of the driveway:
- 8 × 4 = 32 square metres
If each bag covers half a square metre, you will need two bags for each square metre:
- 32 × 2 = 64 bags
First you need to change the width to centimetres. 25 mm is the same as 2.5 cm. Then you can work out the area:
- 2.5 × 4 = 10 square centimetres
There are 80 yeast, so the amount of yeast per square centimetre (yeast/cm2) is:
- 80 ÷ 10 = 8 yeast per square centimetre
The recording sheet should look like this:
| Sample area no. | 21 |
| Date | 17 October |
| Yeast count | 80 |
| Sample dimensions | 2.5 cm × 4 cm |
| Sample area | 10 cm2 |
| Yeast/cm2 | 8 |
The area of forestry land is:
- 4.5 × 2 = 9 square miles
Activity 5: Finding the area of an irregular shape
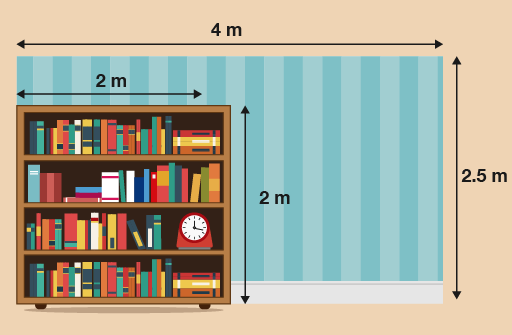
- The estates manager of a college decides to repaint one of the walls in the reception area. The diagram below shows the dimensions of the wall that needs painting.
The wall is 4 m long and 2.5 m high and has a large fixed bookcase in the corner. What is the area of the section of the wall that needs painting?
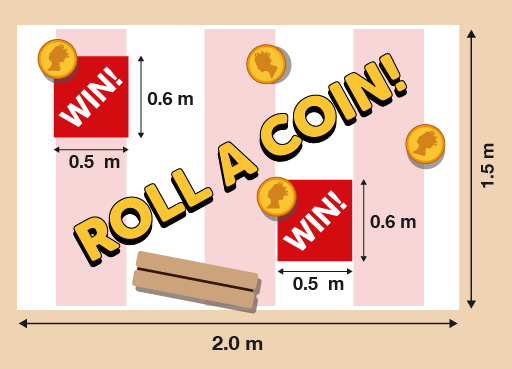
- A charity holds a fundraising fête. A volunteer from the charity designs a game that is played by rolling coins across a table. She marks out two areas labelled ‘WIN!’.
Anyone who rolls a coin into an area labelled ‘WIN!’ will win a prize. But what is the area of the rest of the table?
Answer
First you need to calculate the area of the whole wall:
- 4 × 2.5 = 10 m2
Then you need to calculate the area of the bookcase:
- 2 × 2 = 4 m2
Then subtract the area of the bookcase from the area of the wall:
- 10 – 4 = 6 m2
So the area of the wall that needs painting is 6 m2.
To calculate the non-winning area of the table, first you need to calculate the area of the whole table:
- 1.5 × 2 = 3 m2
Then calculate the area of the ‘WIN!’ areas. One of these is:
- 0.6 × 0.5 = 0.3 m2
There are two ‘WIN!’ areas, so you need to multiply this by 2:
- 0.3 × 2 = 0.6 m2
You then subtract the ‘WIN!’ areas from the complete area of the table:
- 3 – 0.6 = 2.4 m2
So 2.4 m2 of the table is a non-winning area.
Summary
In this section you have learned how to work out the area of a rectangular shape. You have also looked at more complex, compound shapes for calculating area.