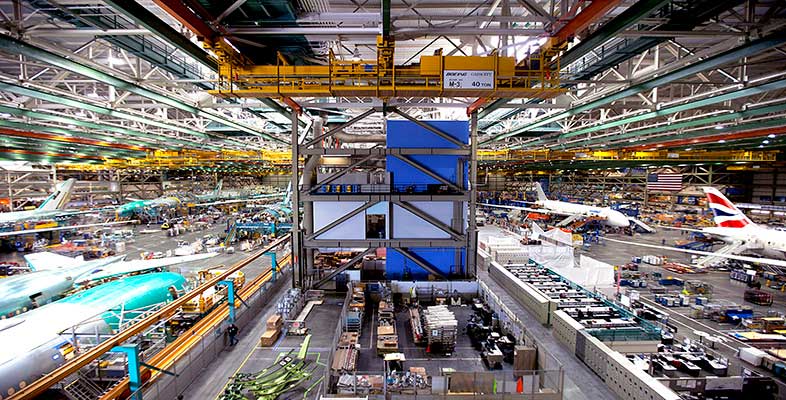
3.4 Transformation processes
A transformation process is any activity or group of activities that takes one or more inputs, transforms and adds value to them, and provides outputs for customers or clients. Where the inputs are raw materials, it is relatively easy to identify the transformation involved, as when milk is transformed into cheese and butter. Where the inputs are information or people, the nature of the transformation may be less obvious. For example, a hospital transforms ill patients (the input) into healthy patients (the output).
Transformation processes include:
changes in the physical characteristics of materials or customers
changes in the location of materials, information or customers
changes in the ownership of materials or information
storage or accommodation of materials, information or customers
changes in the purpose or form of information
changes in the physiological or psychological state of customers.
Often all three types of input – materials, information and customers – are transformed by the same organisation. For example, withdrawing money from a bank account involves information about the customer's account, materials such as cheques and currency, and the customer. Treating a patient in hospital involves not only the ‘customer's’ state of health, but also any materials used in treatment and information about the patient.
One useful way of categorising different types of transformation is into:
manufacture – the physical creation of products (for example cars)
transport – the movement of materials or customers (for example a taxi service)
supply – change in ownership of goods (for example in retailing)
service – the treatment of customers or the storage of materials (for example hospital wards, warehouses).
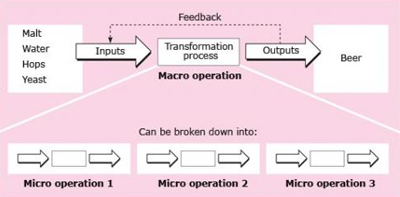
Several different transformations are usually required to produce a good or service. The overall transformation can be described as the macro operation, and the more detailed transformations within this macro operation as micro operations. For example, the macro operation in a brewery is making beer (Figure 2). The micro operations include:
milling the malted barley into grist
mixing the grist with hot water to form wort
cooling the wort and transferring it to the fermentation vessel
adding yeast to the wort and fermenting the liquid into beer
filtering the beer to remove the spent yeast
decanting the beer into casks or bottles.
Activity 5
Identify the principal resources (inputs), the type of transformation process and the principal outputs (goods or services) in each of the following operations.
| Inputs | Type of transformation | Outputs | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refining steel | |||
| Assembling cars | |||
| Delivering cars to dealers | |||
| Repairing cars | |||
| Designing cars |
Discussion
You may have identified various inputs such as materials, energy, machines, equipment, buildings and people. For example, the inputs used by a car assembly plant include components, equipment, buildings, labour and energy. You may also have included less tangible inputs to the transformation process, such as information and skills.
You might have noticed that, midway down the list, the activities changed from primarily the production of goods to the provision of services. In the case of car designing, the principal inputs are ideas and the outputs are materials used to communicate the finished idea, such as blueprints or computer models.