2 Biomass as a solar energy store
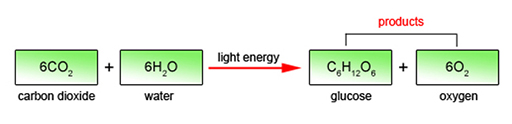
The key mechanism in the use of bioenergy is photosynthesis, in which plants take in carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) from their surroundings and use energy from sunlight to convert these substances into plant biomass.
The essential features of the process can be represented by the chemical equation:
The first product – glucose (C6H12O6), is a carbohydrate, which can be converted within the plant into more complex carbohydrates including starches and cellulose, or can be combined with nitrogen and other elements to form proteins and other components. The second product is oxygen, which is released to the atmosphere.
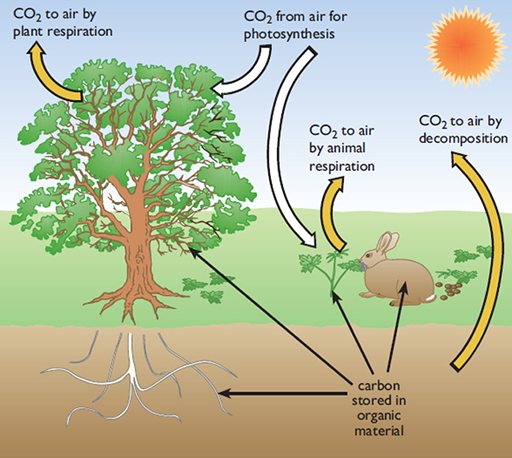
Some of the energy-rich carbohydrate formed is broken down elsewhere in the plant through the process of respiration (photosynthesis in reverse) with oxygen taken in, carbon dioxide given off and energy released. You can see by looking at Figure 3 how this carbon cycle works on a local scale:
How much energy can you obtain from biomass? You’ll look at that in the next section.