Practice Problems Answer Key
Only open this once you've completed the assignment.
All correct answers are in red text.
Practice Problems for Recombinant DNA, Session 2: Basic Mechanism of Cloning
Question 1
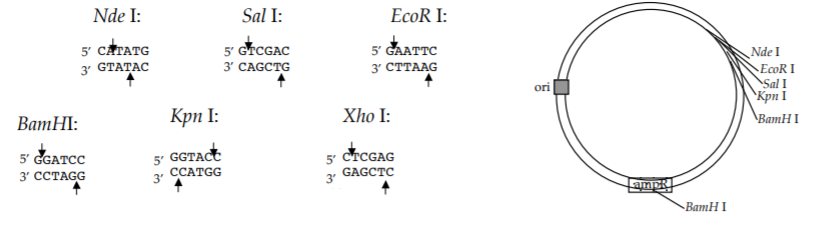
A schematic of the vector p7012 is shown. The restriction enzymes listed cut only where indicated; they do not cut anywhere else in the vector or insert.
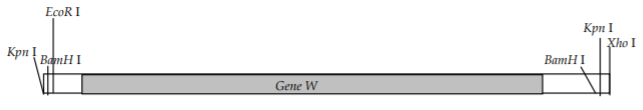
a) A schematic of gene W is below. You want to clone all of gene W DNA into the p7012 vector. Give three different strategies that you could use to clone gene W into p7012, and obtain colonies that contain a recombinant plasmid.
• Strategy 1 uses the restriction enzyme(s) Kpnl to cut the vector and restriction
enzyme(s) Kpnl to cut Gene W
• Strategy 2 uses the restriction enzyme(s) EcoRI and SalI to cut the vector and restriction
enzyme(s) EcoRI and XhoI to cut Gene W
• Strategy 3 uses the restriction enzyme(s) EcoRI and KpnI to cut the vector and restriction
enzyme(s) EcoRI and KpnI to cut Gene W
b) In which of the strategies would Gene W be inserted into the vector in only one direction?
EcoRI/XhoI to EcoRI/SalI or EcoRI/KpnI to EcoRI/KpnI
Question 2
You purify a protein from a plant cell that can act as a potential appetite suppressant. Owing to its possible commercial application you decide to clone the gene, Gene A, that encodes this protein. You isolate this gene from the plant cell, clone it into a plasmid vector and amplify it in the bacterial cells.
a) List three features that a plasmid must have to allow the cloning and amplification of Gene A in bacterial cells.
To clone a gene in a plasmid, the plasmid should have an origin of replication, a site that can serve as the
recognition sequence for restriction enzyme so that the plasmid can be cut open and used as a vector to clone
the desired sequence and a reporter gene (i.e. antibiotic resistant gene) that can be used to differentiate between
the untransformed host cells and the host cells that have obtained the plasmid. (Note: It you also want to express
the gene you will need an appropriate promoter close to the 5’ end of the cloned gene so that the gene will be
expressed and a transcription termination sequence close to 3’ end of the cloned gene to terminate transcription).
b) You decide to use the following plasmid to clone Gene A. To achieve this you digest both the genomic DNA and plasmid DNA using a restriction enzyme. You then ligate the Gene A DNA into the cut plasmids. Finally, you transform the E. coli bacterial cells with the ligation mix (the recombinant plasmids). Note: The recognition sites for Kpn 1 and Sal1 on plasmid are 1 kb apart.
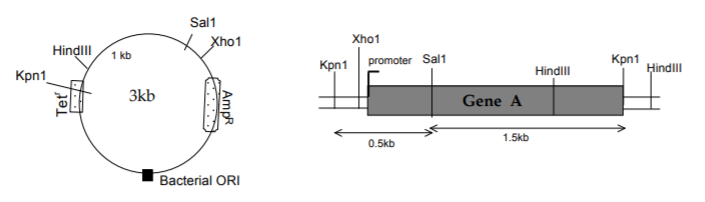
• Which restriction enzyme (Kpn I, Hind III, Sal I or Xho I) did you use to digest Gene A for insertion in to the plasmid?
You would not use Sal 1 and Hind III since they cut within gene A. You would also not use Xho 1 since it
cuts only on one side of gene A. You would use Kpn 1 since it will give you intact gene A with promoter
and has only one recognition site in the plasmid vector.
• Which restriction enzyme (Kpn I, Hind III, Sal I or Xho I) did you use to digest the plasmid before insertion of Gene A? Briefly explain why.
You would use Kpn 1 as well, ensuring that the vector and insert have complementary ends for ligation.
c) You then plate these transformed bacterial cells onto media that will allow you to distinguish between bacterial cells that obtained the plasmid and those that did not. Onto what type of growth medium will you plate your transformation mix? Explain your answer.
You will plate the transformation mix in minimal media that contains ampicillin as the selection marker since the bacterial cells have an intact ampr gene. You will not use tetracycline as the selection marker since the tetr gene is disrupted in the recombinant plasmids that have the Gene A insert.