Beginners’ Chinese: a taster course
Introduction
This free course, Beginners' Chinese: a taster course, is introductory material for absolute beginners in Chinese based on The Open University’s 30-credit module Beginners’ Chinese (L108). This course concentrates on Mandarin Chinese as a tool for communication, but also provides some insights into Chinese society and culture. It contains a brief introduction to the Chinese language, its scripts and sounds, and how words are formed. The language activities and audio extracts presented here are not meant for a complete course, but are samples to give you a taste of what it is like to learn Chinese online with The Open University. You will hear short conversations where people greet each other and introduce themselves, and learn how to count from one to ten. You’ll learn different ways of saying your name and greeting people, as well as give your telephone number.
Before you continue with this course, make sure you have enabled the Chinese font on your computer. Video 1 gives step-by-step instructions on how to do this for both PC and Mac users.
Transcript: Video 1
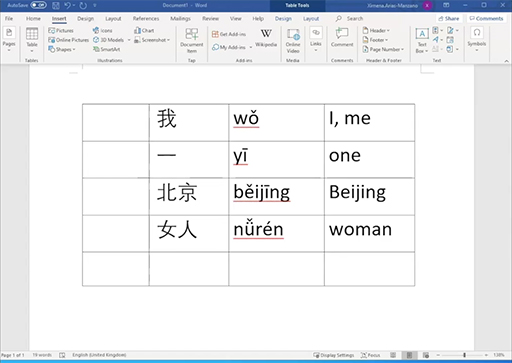
Now watch Video 2 which explains how to type words in Chinese on a computer.
Transcript: Video 2
You may wish to print out the Instructions on how to enable Chinese font and type characters [Tip: hold Ctrl and click a link to open it in a new tab. (Hide tip)] for your own reference. Note that Video 1 and the instructions about enabling Chinese fonts for PC were based on Windows 10. For Windows 11, see Video 3 below.
Please note, to revert back to an English (or your primary language) keyboard on a Windows PC you will need to click on the Chinese character ![]() , which appears in the bottom right hand corner of your computer screen next to the date and time and where you will have originally switched from an English to Chinese keyboard. Once you have clicked on this character you will then be given the option to select the English keyboard. The same rules apply for reverting back to English on a Mac, however the character
, which appears in the bottom right hand corner of your computer screen next to the date and time and where you will have originally switched from an English to Chinese keyboard. Once you have clicked on this character you will then be given the option to select the English keyboard. The same rules apply for reverting back to English on a Mac, however the character ![]() will be found in the top right hand corner or your computer screen, again in the position where you originally switched your keyboard to Chinese.
will be found in the top right hand corner or your computer screen, again in the position where you originally switched your keyboard to Chinese.
Watch the video below for adding Chinese keyboard and typing on Windows 11, MacOS, Android and iOS.
You can also consult Windows Support page for adding the Chinese keyboard for both Windows 10 and Windows 11.
