2.7 Summary
- Accounting records are the day-to-day records of all financial transactions and other relevant financial information concerning a business.
- Financial statements are summaries of accounting records to satisfy the relevant financial information needs of stakeholders of a business.
- The owner(s) of a business is (are) the main stakeholder(s) in a business but there are a number of other stakeholders.
- In accounting terms, the business is a separate entity from its owner(s) even if the business is owned by a sole trader with unlimited liability for the debts of the business.
- In accounting terms, the business is a separate entity from its owner(s) even if the business is owned by a sole trader with unlimited liability for the debts of the business.
- Liabilities are debts owed by the business.
- Capital is the owner’s investment in the enterprise.
- The vertical balance sheet of a business reflects the accounting equation: Assets – Liabilities = Capital.
- Financial transactions have two aspects which must be equal to keep the accounting equation in balance.
- Financial transactions are recorded by debits and credits in the ledger accounts (also known as T-accounts).
- Assets are represented by debit balances while liabilities and capital are represented by credit balances.
- The following rules apply to asset, liability and capital accounts.
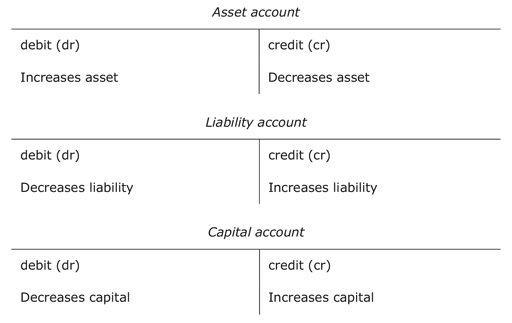
Figure 20
- To calculate the balance in an asset account we calculate the excess of debits over credits to get the net debit balance.
- To calculate the balance in a liability or capital account we calculate the excess of credits over debits to get the net credit balance
- The balance carried down figure within an asset account is always on the credit side of the account and is brought down as a debit balance.
- The balance carried down figure within a liability or capital account is always on the debit side of the account and is brought down as a credit balance.
