5 The orignial course team's approach to systems engineering
5.1 Introduction: the general framework
The general framework of systems engineering adopted in the course consists of: a hierarchy of elements; aims associated within its outputs and process; a set of principles; a division into technical and managerial components of the process.
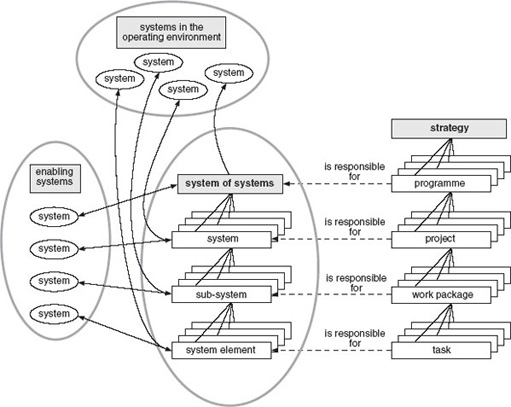
The lexicon of system engineering used in the course contains the hierarchy of elements:
-
strategy: meaning the accumulated decisions concerning the areas in which an organisation operates and its longer-term aims
-
programme: this may be either a single, very large contract or a number of projects that are linked by a business, technological or other logic
-
project: a set of activities required to produce a specified set of outputs
-
work package: a subset of the activities within a project that have a disciplinary (functional), technological or other logic
-
task: a specific activity.
These terms and the levels of activity to which they relate form the hierarchy shown in Figure 47. The relationship of this to the systems structure discussed in the Section 4, and to enabling and operating environment systems, is also indicated. The strategy level of activity is associated with the ‘Enterprise Environment Management Process’ identified in the ISO/IEC 15288 standard.
Various definitions of systems engineering and its characteristics were discussed in Section 2. The definition adopted by the course team is:
Systems engineering is a set of principles, methods and techniques applied to all the tasks involved in all the life cycle stages of a complex system.
