5.5 What is information security?
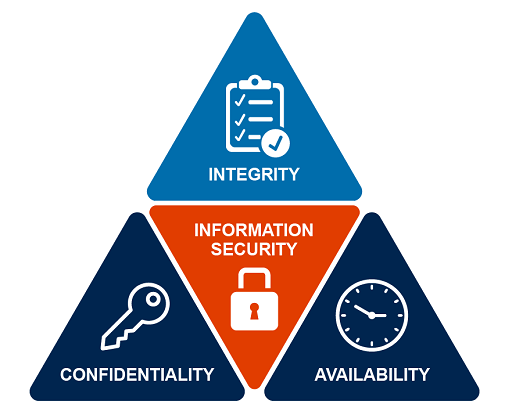
Information security protects the confidentiality, integrity and availability – often referred to as the ‘CIA triad’ – of all assets, information and systems, be they digital or physical.
Below is a brief definition of each element of the triad (based on National Cyber Security Centre [Tip: hold Ctrl and click a link to open it in a new tab. (Hide tip)] , 2021b):
Confidentiality: only authorised personnel in relation to their role should have access to information, to ensure it has not be shared or accessed without permission.
Integrity: information and data needs to be accurate, consistent, and used for its intended purpose. This requires strong non-repudiation and authenticity controls to stop data being modified or destroyed.
Availability: information and data is readily available and there is reliable access to (and use of) information.
The primary focus of information security is to ensure that organisations and individuals operate securely, with minimal disruption to work processes. Achieving this means aiming to reduce the risk of security incidents, which include the theft of, tampering with, or deletion of information and data. Most organisations will have an information security policy that provides guidance on using IT and digital assets safely.