3.9 Addition and subtraction with fractions
Addition and subtraction with fractions can be quite awkward, particularly when fractions are mixed with whole numbers and when the fractions have different denominators. In such cases you may need to use your calculator. However try to gain confidence in handling simple fractions.
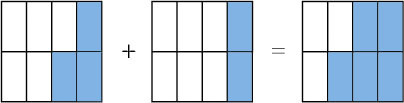
To add two fractions with the same denominator, just add the numerators. For example,
Just as 3 eggs plus 2 eggs is 5 eggs, so 3 eighths plus 2 eighths is 5 eighths.
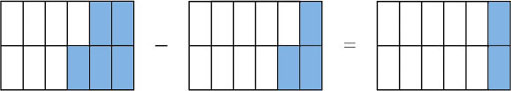
To subtract one fraction from another, where the denominators are the same, just subtract one numerator from the other. For example,
Just as 5 oranges minus 3 oranges is 2 oranges, so 5 twelfths minus 3 twelfths is 2 twelfths,
but is the same as . So the simplest answer is .
However, if the denominators are different, the calculation is a bit more awkward. The first thing to do is to rewrite the fractions as equivalent fractions where the denominators are the same.
A useful mathematical technique with things you can’t immediately handle is to put them in a form where you can handle them.
Example 20
Evaluate
Answer
You cannot add quarters and eighths directly. You need to change them into the same thing.
It is possible to change quarters to eighths.
is equivalent to : .
So make the denominators the same, i.e. both 8.
